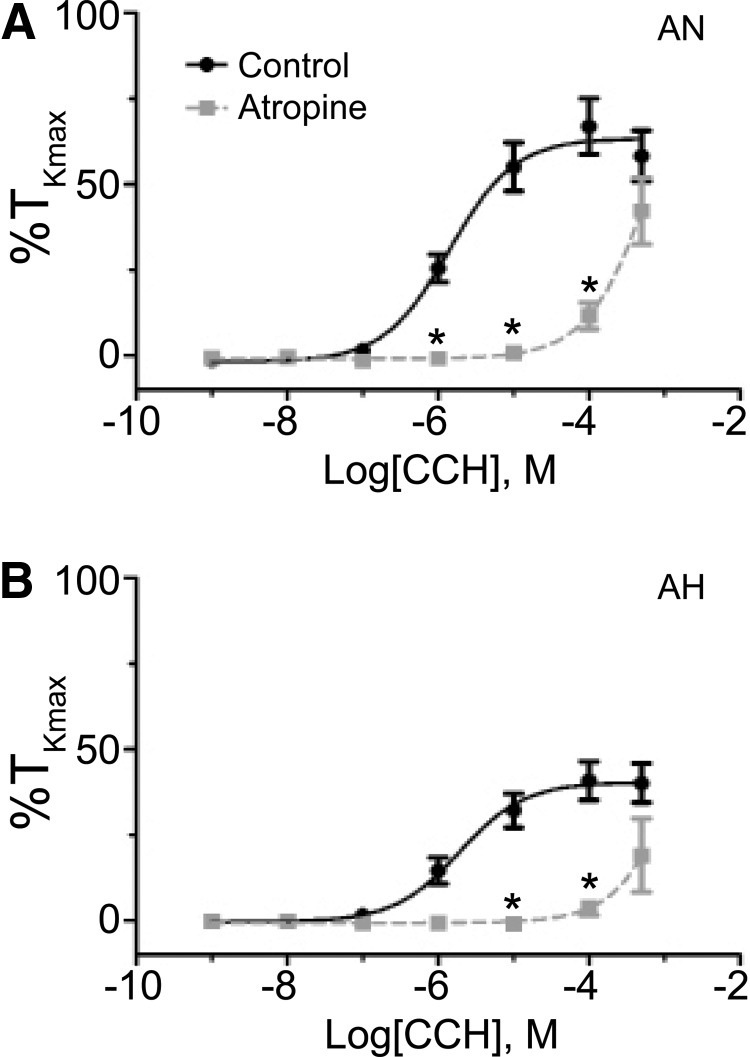
FIG. 5.
Muscarinic receptors are important to carbachol-induced pulmonary arterial contraction. Dose–response contraction curves of pulmonary arterial rings to 1 nm–100 μM carbachol (CCh) added in a cumulative manner normalized to %TKmax following addition of 1 μM atropine for adult normoxic (A) and adult hypoxic (B) pulmonary arteries. The control response is depicted with filled black circles and a solid line, while the atropine response is depicted with filled gray squares and a dashed line. Data are not shown for fetal normoxic arteries due to insufficient response. Lines show resultant fits with a Hill equation to the dose–response relationships, and markers show mean ± SEM. The data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA with a Bonferroni post-test analysis for each dose compared to control. Statistical significance is noted between control and atropine groups (*p < 0.05). Atropine data are based on 20 adult normoxic arteries (7 animals) and 3 adult hypoxic arteries (3 animals).