Figure 1.
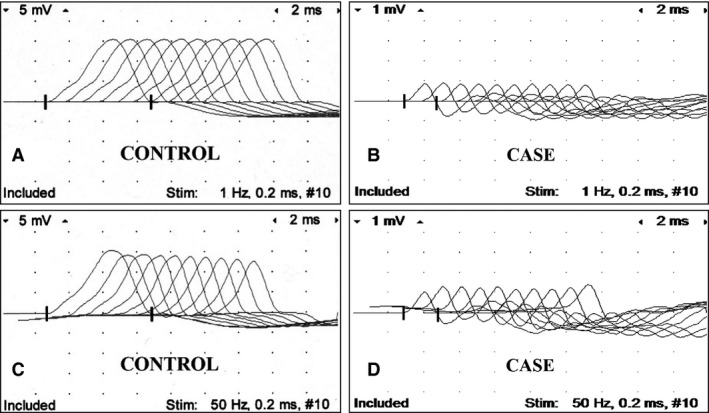
Repetitive nerve stimulation of the peroneal nerve. Control foal at 1 Hz (A), case at 1 Hz (B), control foal at 50 Hz (C), and case at 50 Hz (D). Notice low amplitude of CMAP (compound muscle action potential; B, D) in diseased foal compared to control foal, and sequential increment of CMAP at 50 Hz in diseased foal not present in control foal. Calibration at 5 mV and 1 mV per vertical division in recordings of control and diseased foal, respectively; and 2 ms per horizontal division.
