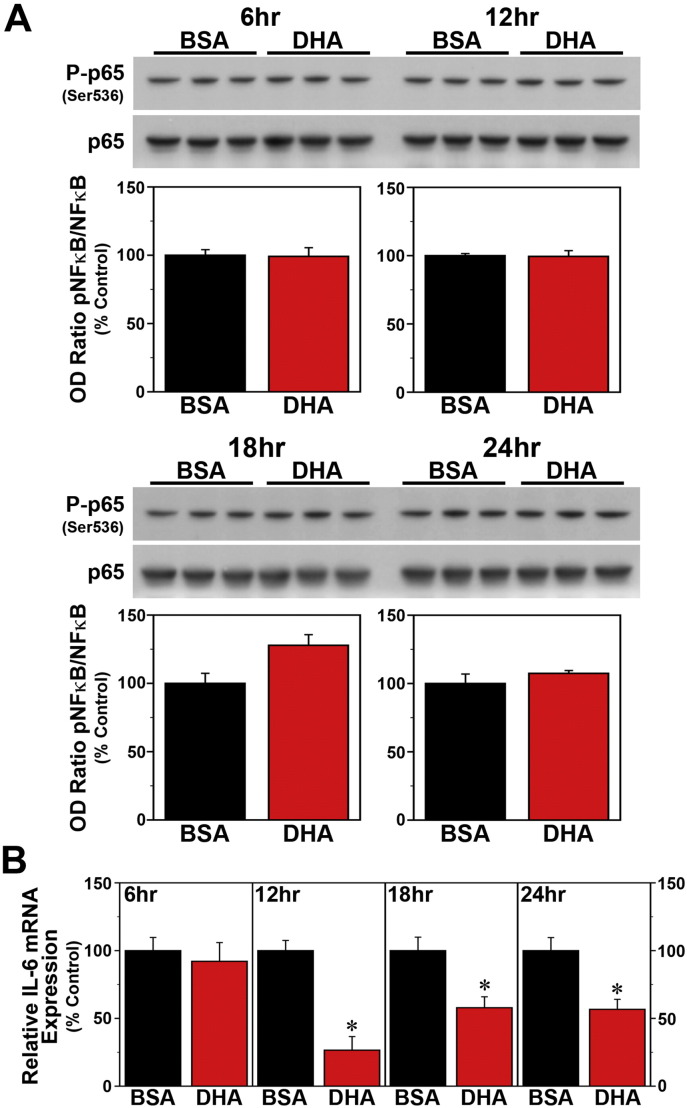
Fig. 6.
Time-dependent effects of acute DHA treatment on inflammatory signaling in Bmal1-dLuc fibroblasts. (A) Representative Western blot and densitometric analyses of NF-κB-mediated inflammatory signaling in fibroblast cultures treated for 4 h with BSA (n = 3) or 250 μM DHA (n = 3) at hours 6, 12, 18 and 24. Bar graphs depict the ratios of P-p65/p65 immunoreactive signal that were adjusted in relation to control (BSA) values (% Control). (B) Real-time PCR determinations (mean ± SEM) of IL-6 mRNA expression in parallel groups of BSA- and DHA-treated fibroblast cultures. Plotted values correspond to the ratio of IL-6 mRNA signal normalized to β-actin mRNA levels in each sample and adjusted relative to the averages of time-matched BSA controls, which were set at 100%. Asterisks denote treatment times in which the relative expression of IL-6 mRNA in DHA-treated fibroblasts was significantly decreased (p < 0.05) in comparison with that found in BSA controls.