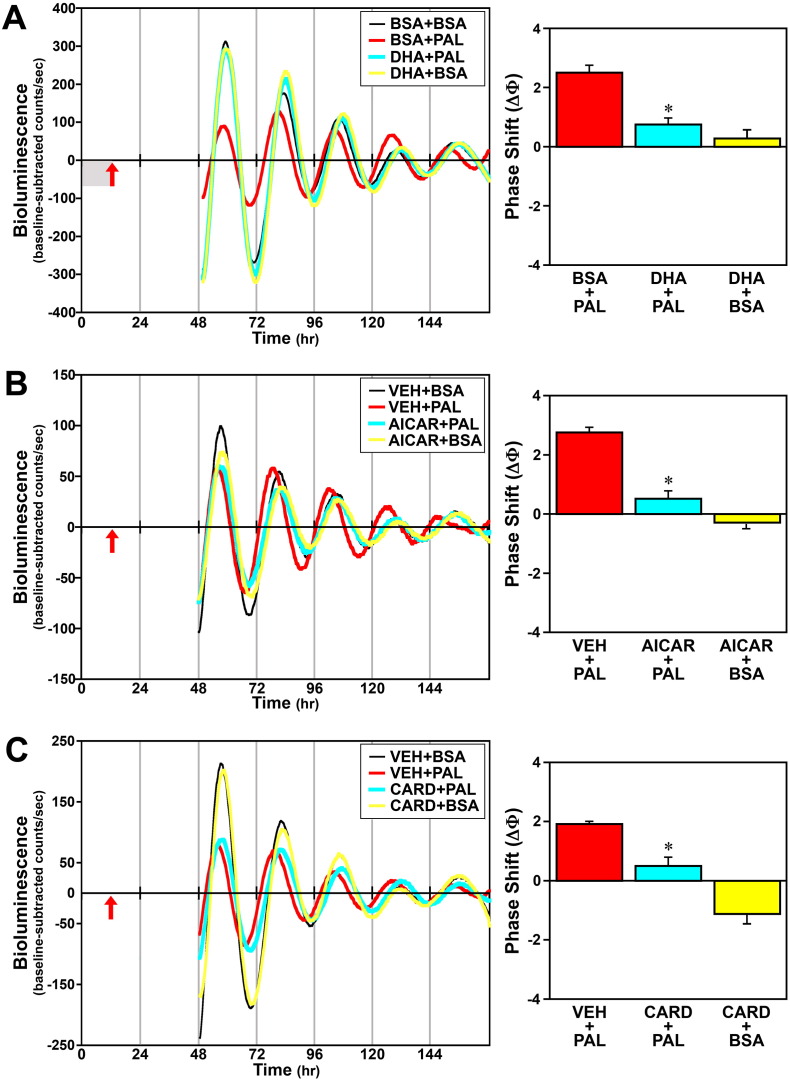
Fig. 11.
Effects of DHA (A), AICAR (B) or cardamonin (C, CARD) treatment on the phase-shifting responses of Bmal1-dLuc fibroblasts to palmitate (PAL). Representative recordings of ensemble bioluminescence from individual fibroblast cultures treated with either vehicle (VEH; DMSO), DHA (50 μM) for 12 h in advance or AICAR (500 μM) or cardamonin (5 μM) for 4 h in conjunction with PAL administration (250 μM) for 4 h at hour 12. Phase-shifting effects of these anti-inflammatory treatments alone were also tested in BSA control cultures treated with DHA for 12 h, or with AICAR or cardamonin for 4 h. Specific experimental groups include: BSA + BSA or VEH + BSA (n = 15), BSA + PAL or VEH + PAL (n = 18), DHA + PAL (n = 6), DHA + BSA (n = 6), AICAR + PAL (n = 10), AICAR + BSA (n = 8), CARD + PAL (n = 6) and CARD + BSA (n = 6). Red arrows denote time of palmitate administration after 12 h pretreatment with DHA (adjacent shaded area in A) or during AICAR (B) or cardamonin treatment (C). Bar graphs depict the mean (± SEM) phase shifts (ΔΦ) in hours as a function of treatment group. Asterisks indicate that palmitate-induced phase shifts were significantly decreased (p < 0.05) in Bmal1-dLuc fibroblasts treated with DHA (DHA + PAL), AICAR (AICAR + PAL) or cardamonin (CARD + PAL) in comparison with those observed in controls (VEH + PAL).