Figure 5.
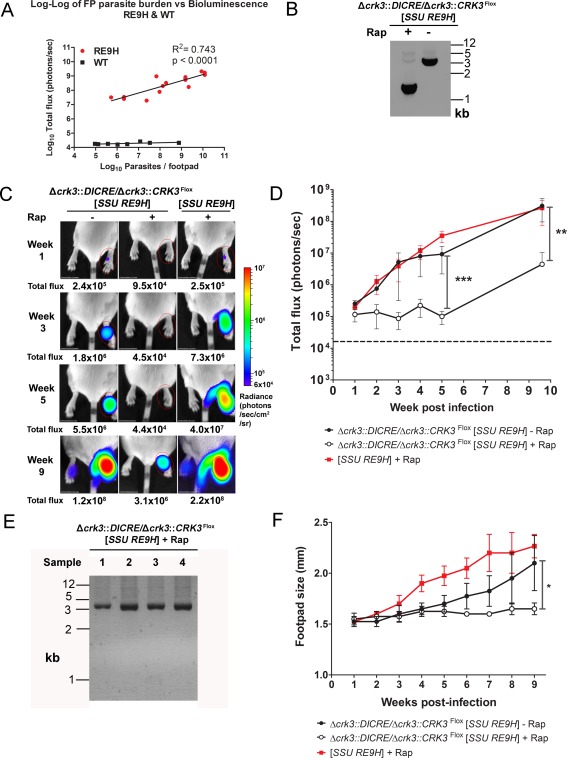
CRK3 conditional deletion in stationary phase promastigotes and in vivo infection.
A. Correlation between in vivo bioluminescence (total flux in photons per second) and parasite burdens from the same infected footpads. BALB/c mice were infected with L. mexicana WT or Ppy RE9H‐expressing stationary phase promastigotes and imaged weekly using an in vivo imaging system (IVIS). At 2, 4, 6 and 8 weeks post‐infection mice were sacrificed after imaging and parasite burdens in infected footpads determined using limiting dilution assays. Each point shows the total flux and parasite burden from the footpad in one mouse (n = 3–4 mice per time point). Linear regression line and R2 was calculated from the log transformed data.
B. PCR amplification of the floxed CRK3 locus of Δcrk3::DICRE/Δcrk3::CRK3 Flox [SSU RE9H] stationary phase promastigotes after incubation in the presence (+) or absence (−) of 1 μM rapamycin for 24 h.
C. Control (−) or 24 h rapamycin‐treated (+) stationary phase promastigotes were inoculated into the footpads of BALB/c mice. The total flux (photons/s) emitted from the infected footpad region of interest (ROI) was quantified weekly.
D. The total flux measured from infected footpads was plotted over 9 weeks of infection. Data shown represent the mean flux and SD from groups of four mice. The dotted line indicates the average background flux emitted from uninfected footpads measured 1 week post infection (n = 12). A significant difference in the mean total flux emitted between the footpads of mice infected with untreated and rapamycin‐induced parasites was observed at 5 and 9 weeks post‐infection (2‐way ANOVA, ***p ≤ 0.001; **p ≤ 0.005).
E. PCR amplification of the floxed CRK3 locus of Δcrk3::DICRE/Δcrk3::CRK3 Flox [SSU RE9H] + Rap after purification of amastigotes from the footpads of 10‐week infected mice. Cells were propagated in vitro to obtain sufficient genomic DNA for PCR analysis.
F. Footpad sizes were recorded by weekly caliper measurement. Data shown represent the mean footpad size and SD from groups of four mice (Unpaired t‐test *p ≤ 0.05).
