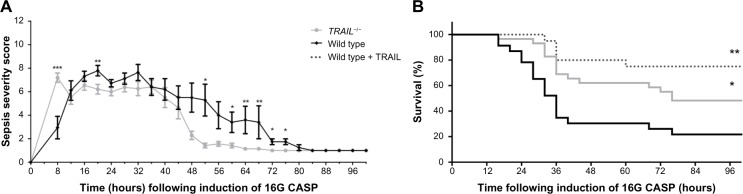
Figure 1.
TRAIL deficiency improved survival in CASP.
Notes: (A) Peritonitis was induced in wild-type and TRAIL−/− mice (n=20 per group). Sepsis severity scores were determined every 4 hours for 100 hours according to Zantl et al.22 Mean values and standard errors of the mean at respective time points are shown for wild-type (black) and TRAIL−/− mice (gray). Eight hours after induction of CASP, TRAIL−/− mice displayed highly significantly increased sepsis severity scores when compared to wild-type mice. In marked contrast, when compared to wild-type mice, sepsis severity was decreased in TRAIL−/− mice from 16 hours until 72 hours following CASP. A representative result of two experiments is shown. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P < 0.001. (B) Peritonitis was induced in wild-type and TRAIL−/− mice (n≥23 per group). An additional group of wild-type mice received TRAIL treatment after induction of CASP (wild type + TRAIL). Survival was monitored every 4 hours. Kaplan–Meier curves are shown for wild-type mice (black), TRAIL-treated wild-type mice (dashed line), and TRAIL−/− mice (gray). TRAIL deficiency significantly improved survival. As previously shown,16 TRAIL treatment highly significantly improved survival after CASP. *P<0.05; **P<0.01 when compared to septic wild-type controls.
Abbreviations: CASP, colon ascendens stent peritonitis; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; TRAIL, TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand.