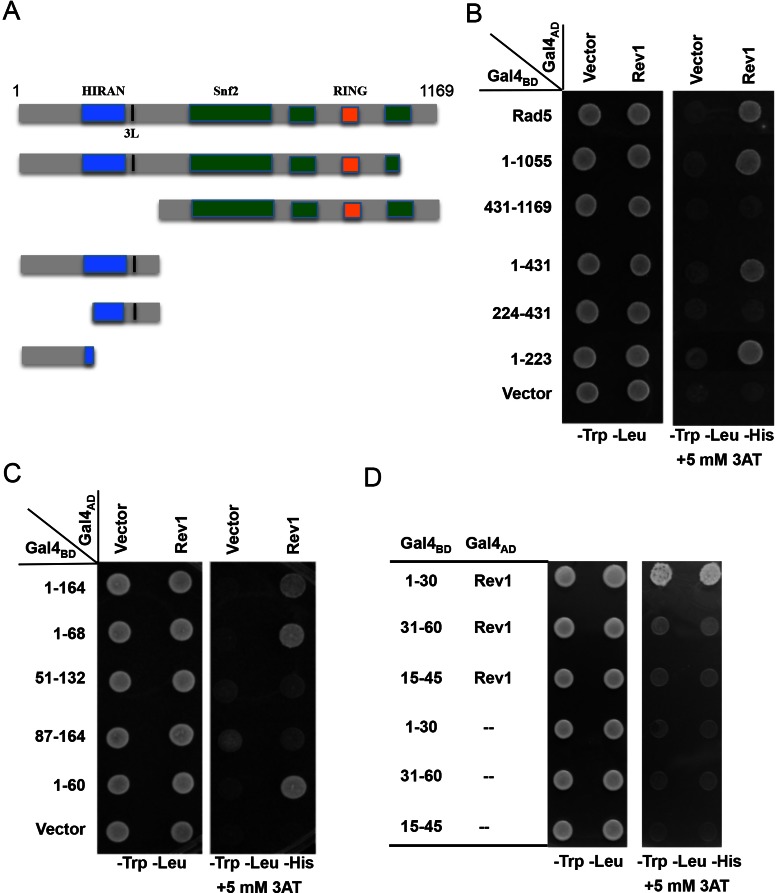
Figure 1.
Mapping the Rev1-binding region in Rad5 by a yeast two-hybrid assay. (A) A diagram indicating Rad5 putative functional domains and the sites of truncation. (B) The Rev1-binding region is mapped to the N-terminal 223 amino acids of Rad5. (C) The Rev1-interacting domain is restricted to the N-terminal 60 amino acids of Rad5. (D) The N-terminal 30 amino acids of Rad5 are sufficient to interact with Rev1. Various combinations of Rad5 truncations and Rev1 as indicated were co-transformed into PJ69-4a. The transformants were spotted on control plates (SD-Leu-Trp) and selective plates (SD-Leu-Trp-His+3AT), which were incubated at 30°C for 4 days before photography. Numbers on the left panel indicate Rad5 amino acid sequences encoded by the pGBT plasmids. Only images from the control plates and selective plates containing 5 mM 3AT are presented.