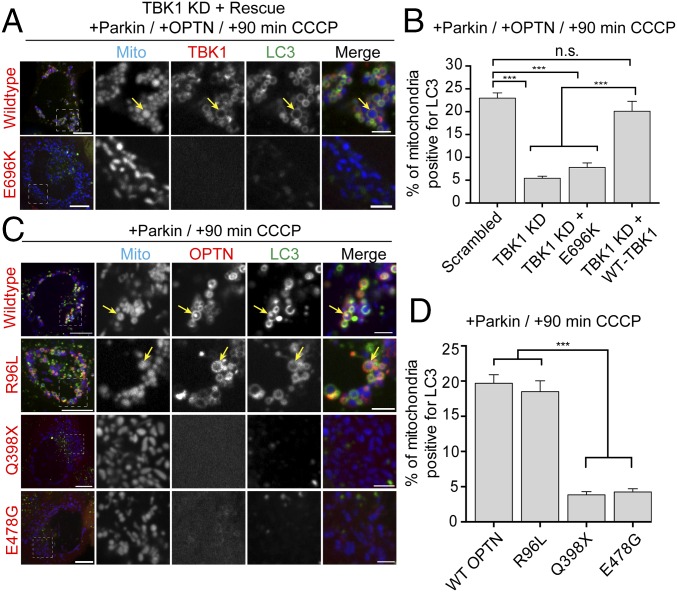
Fig. 9.
ALS-associated TBK1 and OPTN mutants block mitophagy. (A) Representative confocal images of Parkin/OPTN-expressing HeLa cells in which endogenous TBK1 has been knocked down and rescued with either WT-TBK1 or TBK1-E696K. (B) TBK1 depletion significantly blocks mitophagy at 90 min post-CCCP compared with scrambled control. Expression of WT-TBK1, but not ALS-linked TBK1-E696K, rescues this mitophagy defect. (C) Representative confocal images of HeLa cells expressing untagged Parkin, mCherry-LC3 (green), and Mito-SNAP (blue), as well as GFP-OPTN, GFP-OPTN-R96L, GFP-OPTN-E478G, or GFP-OPTN-Q398X (red) at 90 min post-CCCP. Although WT-OPTN and OPTN-R96L colocalize with LC3 on fragmented mitochondria after CCCP treatment (yellow arrows), both OPTN-Q398X and OPTN-E478G remain cytosolic. (D) At 90 min post-CCCP, OPTN-R96L and WT-OPTN enhance mitophagy, whereas cells expressing OPTN-Q398X and OPTN-E478G show significantly lower levels of LC3-positive mitochondria. [Scale bars: A and B (full size), 10 μm; A and B (zoom), 2.5 μm.] Data were collected from 21 to 33 cells from at least thee independent experiments. Bars represent mean ± SEM. ***P < 0.001.