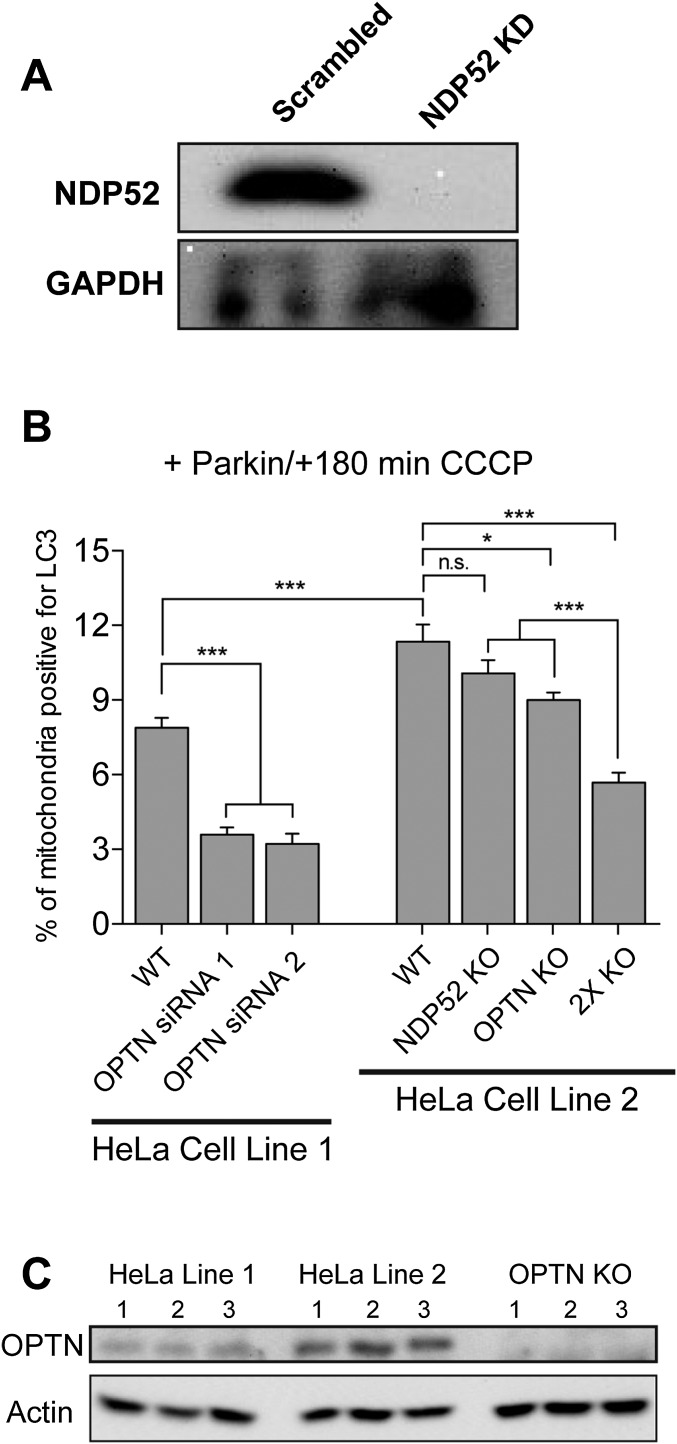
Fig. S4.
(A) Treatment with 100 nM siRNA targeting NDP52 resulted in >95% depletion of endogenous NDP52. (B) Effects of OPTN depletion by transient knockdown and knockout. In the HeLa cell line in standard use in our laboratory (HeLa Line 1), transient knockdown of OPTN with either of two siRNA oligos significantly reduces the engulfment of mitochondria into autophagosomes 3 h post-CCCP treatment. We also used live-cell microscopy to examine mitophagy in OPTN knockout cells from Lazarou et al. (13). At 180 min post-CCCP, OPTN knockout cells display significantly decreased mitophagy compared with the HeLa cell line from which they were generated (HeLa Line 2). Although knockout of NDP52 did not induce a significant defect in mitophagy, we did observe a more pronounced defect in the double-knockout cells, suggesting that NDP52 may only partially compensate for loss of OPTN at shorter time points following mitochondrial depolarization (180 min as shown here), but can compensate more fully at longer time points, such as 24 h in the study of Lazarou et al. (13). (C) Of note, there is a significant difference in baseline mitophagy levels 180 min post-CCCP between the two parental cell lines (HeLa line 1 and HeLa Line 2), which may result from differences in endogenous expression levels of autophagy receptors. Bars represent mean ± SEM. Data were collected from at least three independent experiments. *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001. n.s., not significant.