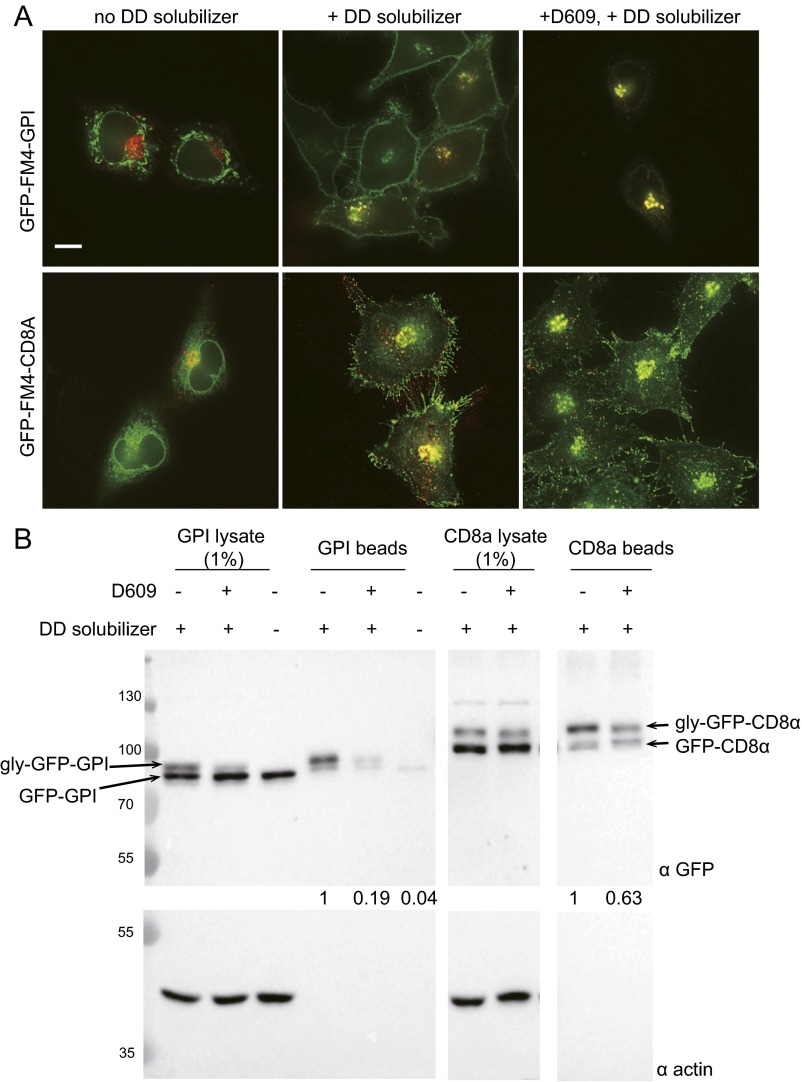
Fig. S4.
Inhibition of SM synthesis results in accumulation of GPI in the Golgi. (A) HeLa cells expressing GFP-FM4-GPI or GFP-FM4-CD8α (and Eqt-SM-mKate2) were incubated with D609 for 3 h before addition of the solubilizer molecule to release GPI and CD8α into the secretory pathway. In the absence of the disaggregating molecule (Left, “no solubilizer”), GPI or CD8α is retained in the ER. In the absence of D609, at 45 min after addition of disaggregating molecule (Center, “+ solubilizer”), both GPI and CD8 localize prominently to the plasma membrane. In cells incubated with D609 for 3 h before addition of disaggregating molecule (Right, “+ D609 + solubilizer”), GPI accumulates in the Golgi, whereas CD8α continues to be delivered to the plasma membrane. (Scale bar: 10 μm.) (B) Surface biotinylation of cells prepared as described in A. After incubation of cells with a membrane-impermeable biotinylation reagent, lysates were generated (1% shown), and biointylated proteins were captured on NeutrAvidin beads. Captured proteins were resolved and observed by SDS/PAGE and anti-GFP immunoblotting. Arrows indicate the positions of the unmodified and secreted, glycosylated (gly) forms of the proteins. Anti-actin blots report cell integrity. Molecular mass standards (kDa) are indicated.