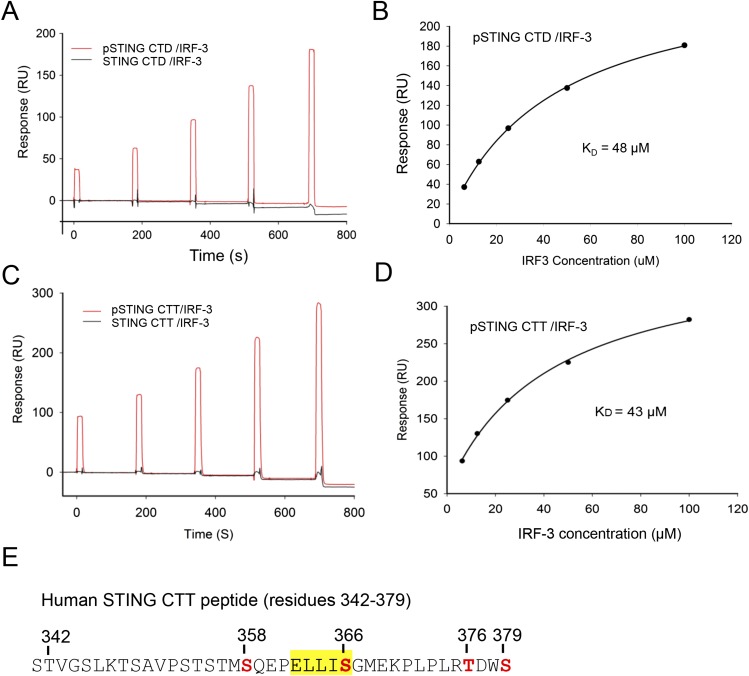
Fig. S1.
SPR-binding studies of the pSTING CTD and CTT with IRF-3. (A) SPR binding studies of the phosphorylated and unphosphorylated STING CTD with IRF-3. (B) Binding affinity between the pSTING CTD and IRF-3. The Kd was determined by fitting the binding data to a one-site binding model. (C) SPR binding studies of the phosphorylated and unphosphorylated STING CTT (residues 342–379, F378W) with IRF-3. The F378W mutation was introduced into human STING CTT for quantification purposes. This mutant peptide also was used for structural analysis. (D) Binding affinity of the pSTING CTT (residues 342–379, F378W) and IRF-3. The Kd was determined by fitting the binding data to a one-site binding model. (E) Potential phosphorylation sites (red) within the pSTING CTT (residues 342–379, F378W). The phosphorylation sites were identified by MS analysis of the pSTING CTT. The pLxIS motif is highlighted in yellow.