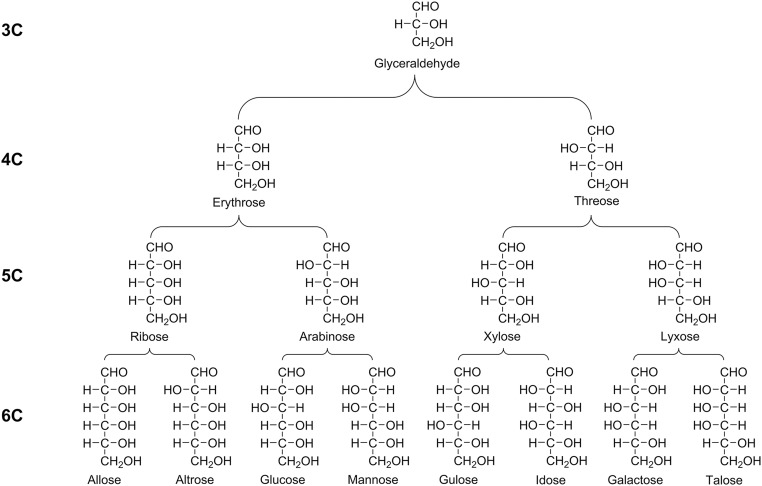
Fig. S5.
The structural relationships of homologous 3C through 6C straight-chained aldehyde (aldo) sugars (only d enantiomers are shown). Upon mild oxidation or alkaline hydrolysis of an individual sugar, a predictable set of homologous degradation products (sugar acids) is observed. For example, upon oxidation of mannose, observed compounds include mannonic acid (trace amounts) → arabinonic acid → erythronic acid → glyceric acid; for talose, compounds include talonic acid (trace amounts) → lyxonic acid → threonic acid → glyceric acid. Arrows are not definite indicators of the order of product formation. Degradation products are observed to retain the d/l ratio of the starting sugar (Fig. S6).