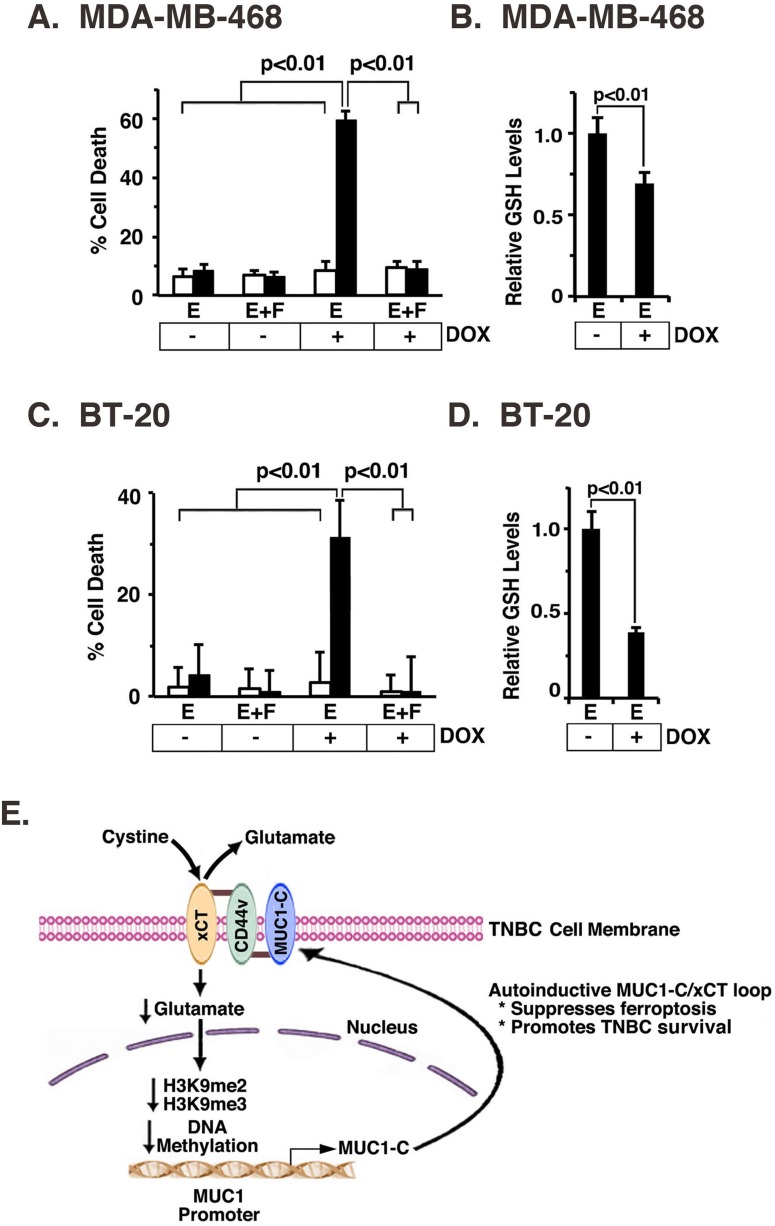
Figure 7. MUC1-C protects against erastin-induced ferroptosis.
A. and B. MDA-MB-468/tet-CshRNA (open bars) and MDA-MB-468/tet-MUC1shRNA (solid bars) cells were treated with 200 ng/ml DOX for 7 d. A. Cells were then plated in a 96 well plate, and exposed to 1 μM erastin (labeled E) with or without 2 μM Fer-1 (labeled F) for 24 h. The results (mean±SD of 8 determinations) are expressed as percentage cell death as determined by Alamar blue analysis. B. The indicated cells were analyzed for relative GSH levels (mean±SD of 3 determinations) as compared with that obtained for erastin-treated, DOX- cells (assigned a value of 1)(right). C. and D. BT-20/tet-CshRNA (open bars) and BT-20/tet-MUC1shRNA (solid bars) cells were treated with 200 ng/ml DOX for 7 d. C. Cells were then plated in a 96 well plate, and exposed to 0.5 μM erastin (labeled E) with or without 2 μM Fer-1 (labeled F) for 12 h. The results (mean±SD of 8 determinations) are expressed as percentage cell death as determined by Alamar blue analysis. D. The indicated cells were analyzed for relative GSH levels (mean±SD of 3 determinations) as compared with that obtained for erastin-treated, DOX- cells (assigned a value of 1)(right). E. Schema of the proposed MUC1-C/xCT regulatory loop. MUC1-C forms a complex with xCT and CD44v in the TNBC cell membrane through a direct interaction between the MUC1-C cytoplasmic domain (MUC1-CD) and the CD44v intracellular domain (CD44v-ICD). CD44v interacts with xCT through their extracellular domains [7]. MUC1-C stabilizes xCT; thus targeting MUC1-C decreases xCT in the cell membrane. In addition, targeting xCT with silencing or SASP increases intracellular glutamate and thereby suppresses MUC1 transcription by increasing H3K9 and DNA methylation on the MUC1 promoter. The MUC1-C/xCT loop suppresses ferroptosis and promotes TNBC cell survival.