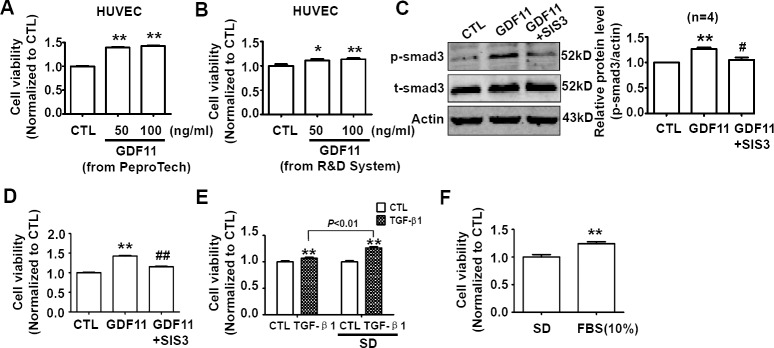
Figure 10. Effects of GDF11 on cell viability of HUVECs in serum-deprivation culture condition.
A. GDF11 (50ng/ml and 100ng/ml) purchased from PeproTech increased cell viability of HUVECs after 24h treatment in serum-deprivation culture condition. **P < 0.01 vs. control. n = 36. B. GDF11 (50ng/ml and 100ng/ml) purchased from R&D Systems increased cell viability of HUVECs after 24h treatment in serum-deprivation culture condition.*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. control. n = 12. C. SIS3 (5μM) inhibited GDF11-induced smad3 activation in HUVECs. The cells were pre-treated by SIS3 (5μM) for 1h and then GDF11 (50ng/ml) was added. **P < 0.01 vs. control. # P < 0.05 vs. GDF11 treatment group. D. SIS3 (5μM) inhibited GDF11-induced increase of cell viability of HUVECs in serum-deprivation culture condition. **P < 0.01 vs. control. ## P < 0.01 vs. GDF11 treatment group. n = 36. E. TGF-β1 (100ng/ml) increased cell viability in normal and serum-deprivation culture condition after 24h treatment. The effect of increasing cell viability was more significant in serum-deprivation (SD) than in normal culture condition after 24h treatment. **P < 0.01 vs. control. n = 24. F. Fetal bovine serum (10%) supplement increased cell viability comparing with serum-deprivation condition. **P < 0.01 vs. control. n = 12. FBS, fetal bovine serum.