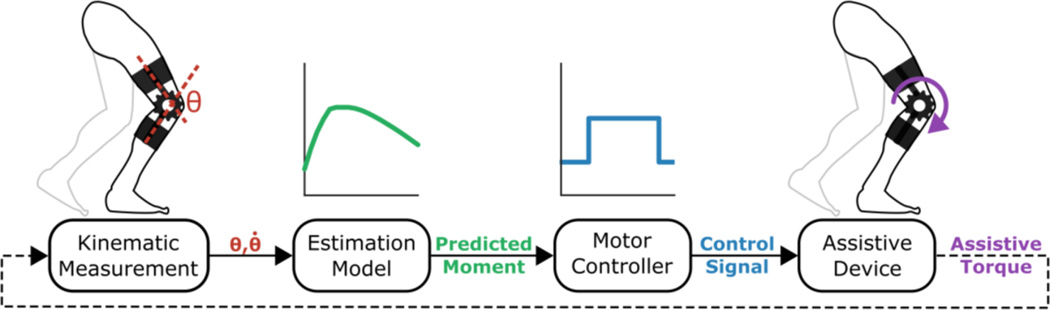
Figure 1.
A framework for utilizing the estimated instantaneous knee extensor moment in the adaptive control of a robotic knee orthosis. On-board sensors measure the knee joint kinematics, which are input into an estimation model to determine the instantaneous internal knee joint moment. The predicted moment is used by the motor controller to specify the necessary control signals to elicit the motor torque for the desired level of assistance as a percentage of the internal knee joint moment.