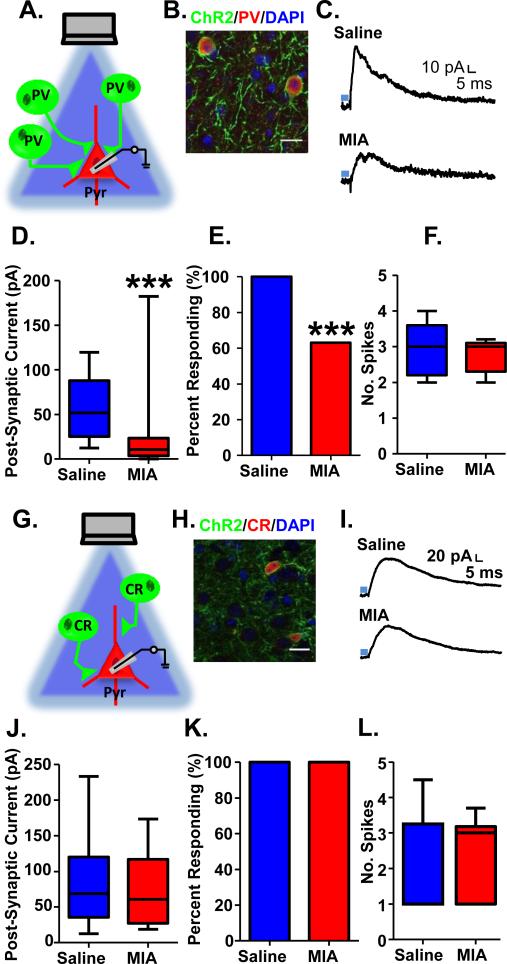
Figure 2.
Decreased light-evoked PV GABAergic transmission onto pyramidal cells in mPFC of adult MIA offspring. (A) Schematic illustrating experiment in PV-ChR2 mice. (B) ChR2-YFP (green) is expressed exclusively in PV interneurons (red; DAPI-labeled nuclei are shown in blue). (C) Example traces showing inhibitory post-synaptic currents (IPSCs) recorded in pyramidal cells from the mPFC of adult Saline and MIA offspring evoked by 5 ms stimulation with 470 nm blue light (blue bar) at a holding potential of −70 mV. (D) The amplitude of the light-evoked IPSCs as well as (E) the percent of pyramidal cells showing a significant light-evoked IPSC response was significantly decreased in the MIA offspring. (F) The number of spikes evoked by 5 ms of light-stimulation of ChR2-expressing PV cells in the mPFC of adult MIA offspring was unchanged. (G) Schematic illustrating experiment in CR-ChR2 mice. (H) ChR2-YFP (green) is expressed exclusively in CR interneurons (red; DAPI-labeled nuclei are shown in blue). (I) Example traces showing inhibitory post-synaptic currents (IPSCs) recorded in pyramidal cells from the mPFC of adult Saline and MIA offspring evoked by 5 ms stimulation with 470 nm blue light (blue bar) in the presence of 20 μM CNQX and 50 μM AP5 at a holding potential of −50 mV. (J) The amplitude of the light-evoked IPSCs as well as (K) the percent of pyramidal cells showing a significant light-evoked IPSC response was unchanged in the MIA offspring. (L) The number of spikes evoked by 5 ms of light-stimulation of ChR2-expressing CR cells in the mPFC of adult MIA offspring was unchanged. ***p<0.001. Scale bar = 20 μm. (See also Supplementary Figure S1 and S2).