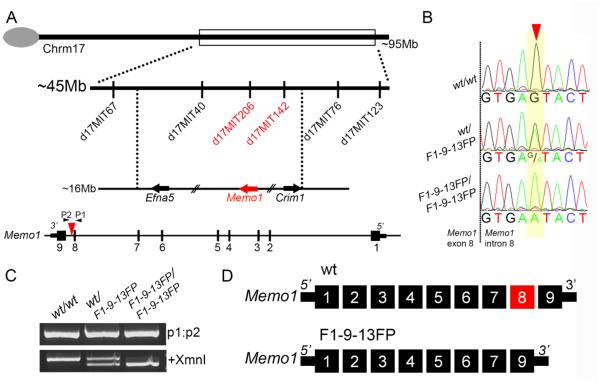
Figure 2. Mapping and exome sequencing identifies a point mutation in Mediator of ErbB2 driven cell motility 1 associated with the F1-9-13FP phenotype.
A) Top: Schematic of mouse chromosome 17 showing markers used to map the position of the ENU induced mutation in F1-9-13FP embryos. Bottom: Schematic of the Memo1 locus showing relative location of point mutation (red arrowhead in intron 8). Note direction of transcription is shown from right to left to match chromosomal arrangement. B) Representative chromatograms of sequencing results from genomic DNA of wild-type as well as F1-9-13FP heterozygous and homozygous embryos, with position of the single nucleotide transition in intron 8 of Memo1 shown by red arrowhead. C) Gel electrophoresis of PCR products generated using primers (P1 and P2 in Fig 2A) flanking the ENU induced mutation and genomic DNA from wild-type as well as F1-9-13FP heterozygous and homozygous embryos. Prior to size separation a portion of the PCR product was digested with XmnI restriction enzyme (lower gel). D) Schematic of the nine exon wild-type Memo1 mRNA transcript as well as the major mRNA splice product produced in F1-9-13FP mutants, namely an in-frame deletion of the exon 8 (for clarity, the orientation of the transcript has been reversed from that shown in A).