Figure 3. The cloned metabotropic 5-HT2A, 5-HT2C and 5-HT6 receptors are potently activated by serotonin.
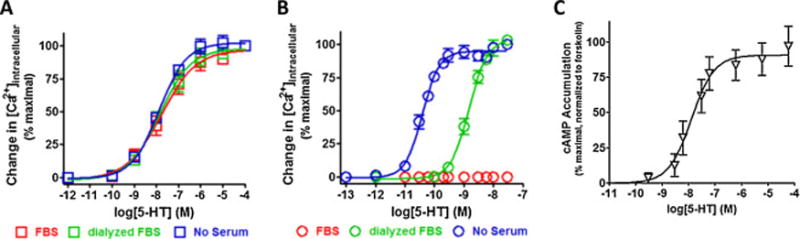
Functional dose-responses to serotonin for the Gq-coupled 5-HT2 receptors were measured as an increase in intracellular calcium using the calcium sensitive fluorescent dye Calcium-6 QF (Ex485/Em525), while the functional dose-response for the Gs-coupled 5-HT6 receptor was measured as an increase in cAMP detected using the bioluminescent cAMPGlo assay. All data are presented as averaged values from multiple experiments ± SEM. A, Serotonin activates the 5-HT2A receptor with an average potency (EC50) range from 13–17 nM and a pseudo Hill slope range from 0.55–0.70 that was insensitive the serum condition used for culturing (P > 0.05 ANOVA with with a Bonferroni post-hoc). B, Serotonin activates the 5-HT2C receptor with a potency (EC50) = 1.5 ± 0.18 nM and a pseudo Hill slope = 1.4 ± 0.19 when cells were cultured in dialyzed FBS and a potency (EC50) = 0.039 ± 0.0039 nM and a pseudo Hill slope = 1.5 ± 0.17 when cells were cultured in absence of serum. No response was observed when cells were culture in FBS. C, Serotonin activates the 5-HT6 receptor with a potency (EC50) = 12.7 ± 6.2 nM and a pseudo Hill slope = 1.02 ± 0.35.
