Figure 3.
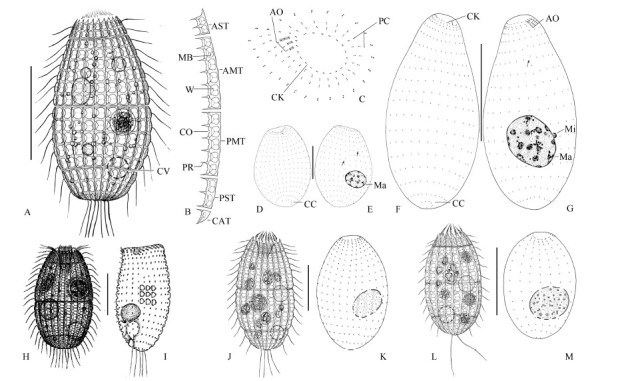
Morphology and infraciliature of the Chinese population (A-G) and South Korean population (J, K) of Levicoleps biwae jejuensis, L. biwae biwae (H, I) , and L. taehwae (L, M)

Morphology and infraciliature of the Chinese population (A-G) and South Korean population (J, K) of Levicoleps biwae jejuensis, L. biwae biwae (H, I) , and L. taehwae (L, M)