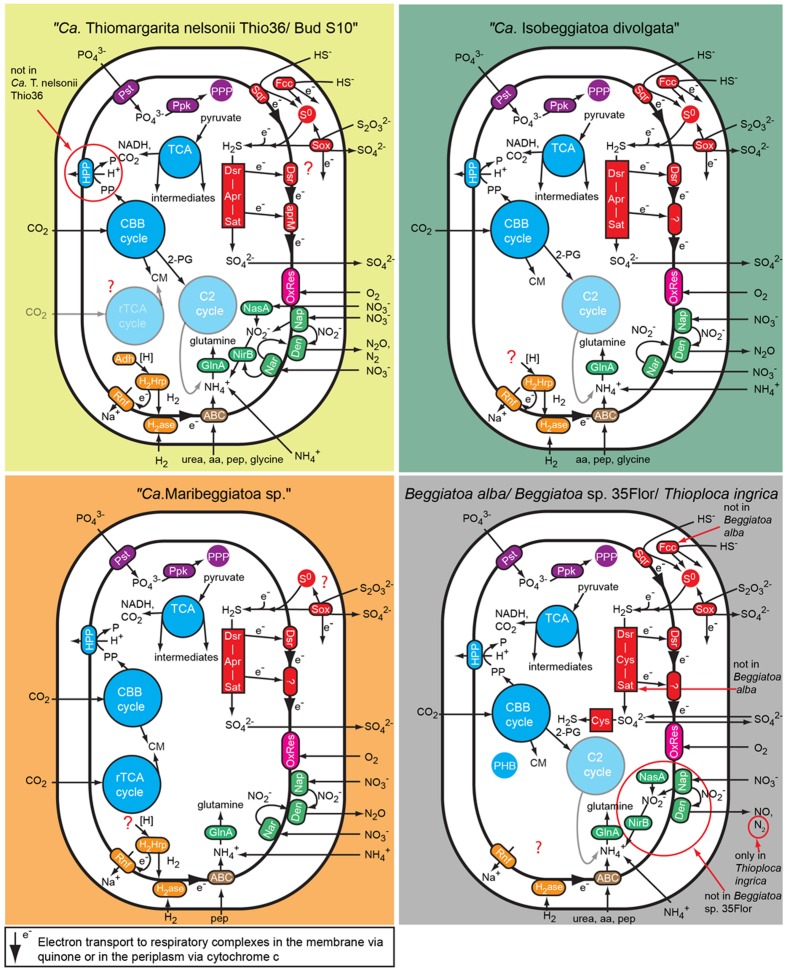
FIGURE 2.
Comparison of C, N, S, P, and energy pathways in the investigated large, colorless LSB based on the genomic information. Note that not all genes essential for some of the predicted pathways have been found in the genomes because of the fragmented nature of most genomes. Aa, amino acid; ABC, ABC transporter; Adh, alcohol dehydrogenase; Apr, APS reductase; CBB cycle, Calvin-Benson-Basshman cycle; C2 cycle, glyoxylate cycle; CM, cell material; Cys, 3″ phosphoadenylylsulfate reductase; Den, denitrification proteins; Dsr, dissimilatory sulfite reductase and related proteins; Fcc, flavocyctochrome c; GlnA, Glutamine synthetase; H2ase, uptake hydrogenase; H2Hrp, methyl viologen-reducing hydrogenase:heterodisulfide reductase complex; HPP, proton translocating pyrophosphatase; Nar, membrane-bound respiratory nitrate reductase; Nap, periplasmatic respiratory nitrate reductase; NasA, assimilatory nitrate reductase; NirB, assimilatory and dissimilatory nitrite reductase; OxRes, oxygen respiration; pep, peptides; PHB, polyhydroxybutyrate granule; PPP, polyphosphate granule; Ppk, polyphosphate kinase; Pst, phosphate transport system; Rnf, membrane-bound electron transport complex; rTCA, reductive tricarboxylic acid cycle; S0, sulfur globules; Sat, ATP sulfurylase; Sox, SOX enzyme complex; Sqr, sulfide quinone reductase; TCA, tricarboxylic acid cycle.