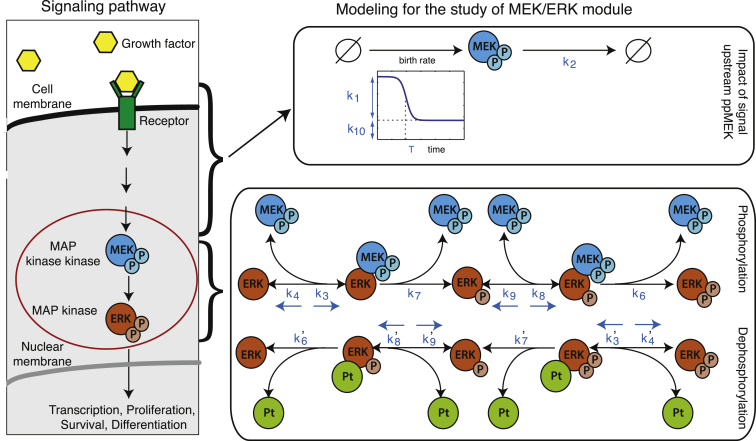
Figure 1.
The MEK/ERK System and Modeling of the MEK/ERK Module
The binding of a growth factor to its receptor activates a succession of reactions that lead to the phosphorylation of MEK; active MEK, in turn, phosphorylates ERK. In this study, we focus on the MEK/ERK module (circled in red). The impact of the stimulus and the upstream reactions on the evolution of the concentration of active MEK are modeled using a time-dependent function, which depends on three parameters (k1, k10, and T). In addition, active MEK is degraded with rate k2. The detailed mechanism of phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of ERK is represented in the bottom-right part of the figure. Pt denotes the cognate ERK phosphatase. The reaction rates are shown next to their associated reactions.