Table 1.
Plasmids used and designed in this study.
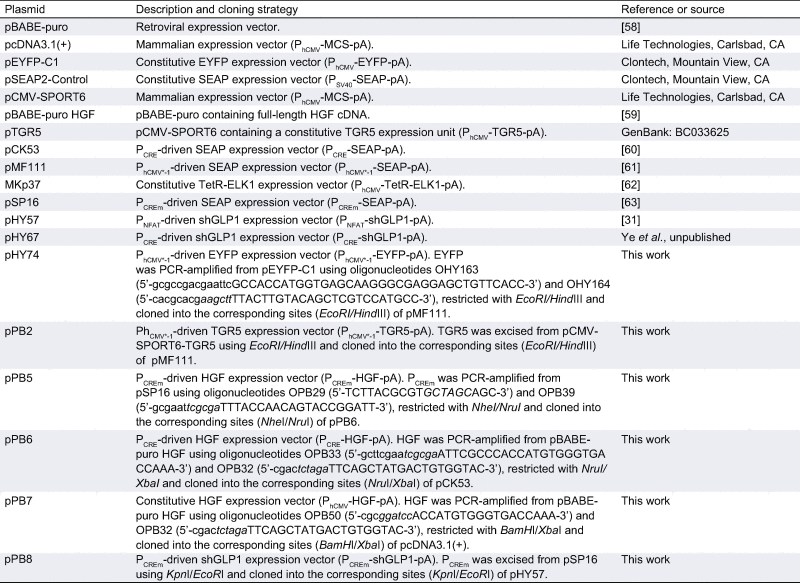 |
CRE, cAMP-response element; CREm, modified cAMP-response element; ELK1, ETS domain-containing transcription factor; ETS, E26 transformation-specific or E-twenty-six transcription factor family; EYFP, enhanced yellow fluorescent protein; HGF, human hepatocyte growth factor; MCS, multiple cloning site; NFAT, nuclear factor of activated T cells; pA, polyadenylation signal; PCRE, CRE containing synthetic mammalian promoter; PCREm, modified PCRE variant; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; PhCMV, human cytomegalovirus immediate early promoter; PhCMVmin, minimal version of PhCMV; PhCMV∗-1, tetracycline-responsive promoter (tetO7-PhCMVmin); PNFAT, synthetic mammalian promoter containing a NFAT-response element; PSV40, simian virus 40 promoter; TetR, Escherichia coli Tn10-derived tetracyclinedependent repressor of the tetracycline resistence gene; tetO7, TetR-specific heptameric operator sequence; TetR-ELK1, TetR-ELK1 fusion protein; SEAP, human placental secreted alkaline phosphatase; shGLP1, short human glucagon-like peptide 1; TGR5, human bile acid receptor (GenBank: BC033625) also known as GPBAR1 (G protein–coupled bile acid receptor 1) or M-BAR (membrane-type receptor for bile acids).
Oligonucleotides: Restriction endonuclease-specific sites are in italics and annealing base pairs are indicated in capital letters.
