Figure 2.
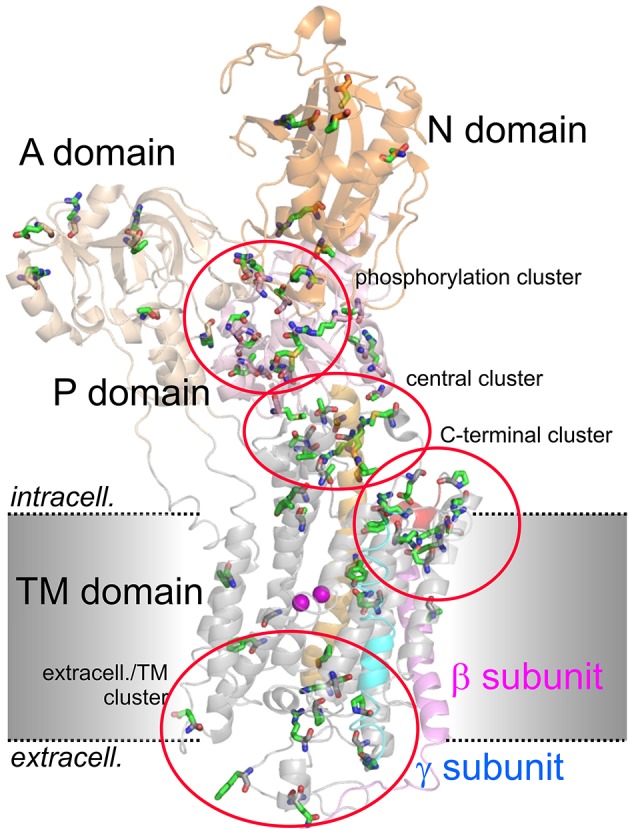
Structure of the Na+,K+-ATPase (PDB code 3B8E; Morth et al., 2007) and location of migraine-associated ATP1A2 mutations. The domains of the cytoplasmic part are A (actuator; light orange), N (nucleotide binding; orange) and P (phosphorylation; pink) domain, transmembrane helices are depicted in gray, except for the about 70 Å-long central TM5 helix (orange). The β- and γ-subunits are shown in magenta and blue, respectively, two Rb+ ions in the cation binding pocket are shown as purple spheres. Amino acids mutated in migraine cases as listed in Supplementary Table 1 are shown in stick representation. More than 80% of mutations fall into four clusters, one around the catalytic P domain, one in a central region between P and TM domain, one within the extracellularly-facing part of the TM domain, and one around the enzyme's C-terminus.
