Figure 3.
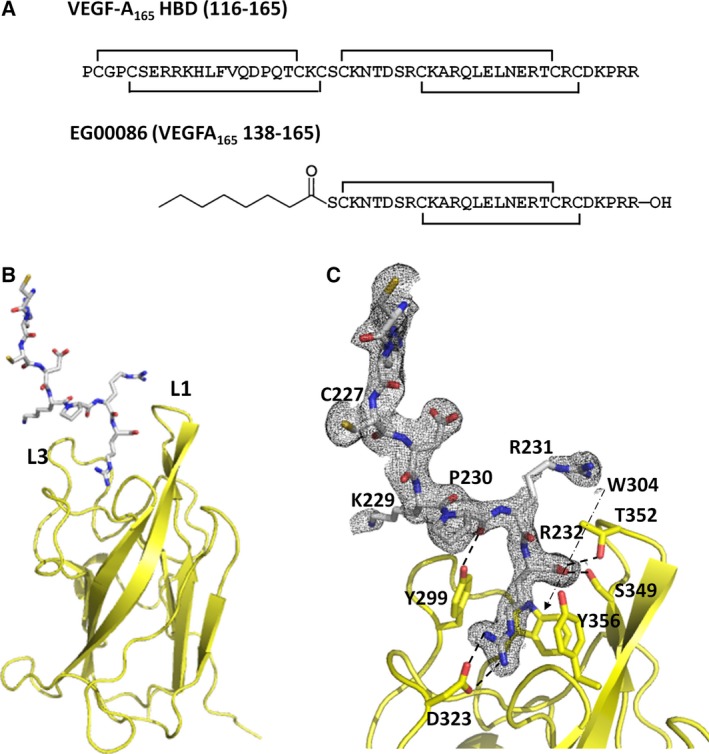
Structure of the VEGF‐A165‐derived peptide bound to the NRP2 b1 domain. (A) The amino acid sequences of the heparin binding domain of VEGF‐A165 and the related bicyclic peptide EG00086. Disulfide links are indicated. The numbering corresponds to the full‐length VEGF‐A form. (B) A maximum of eight C‐terminal residues of EG00086 (sticks) were detected in the electron density maps of the molecular complex. The peptide binds to the canonical ligand binding site flanked by loops L1 and L3. (C) Detailed view of the interactions between the peptide and NRP2. Relevant residues have been labelled, and the specific hydrogen bonds and charge–charge interactions are indicated by dashed lines. The 2 F o – F c electron density map (grey mesh) showed significant disorder for the peptide region; in this image, the associated electron density map is contoured at 0.6 σ.
