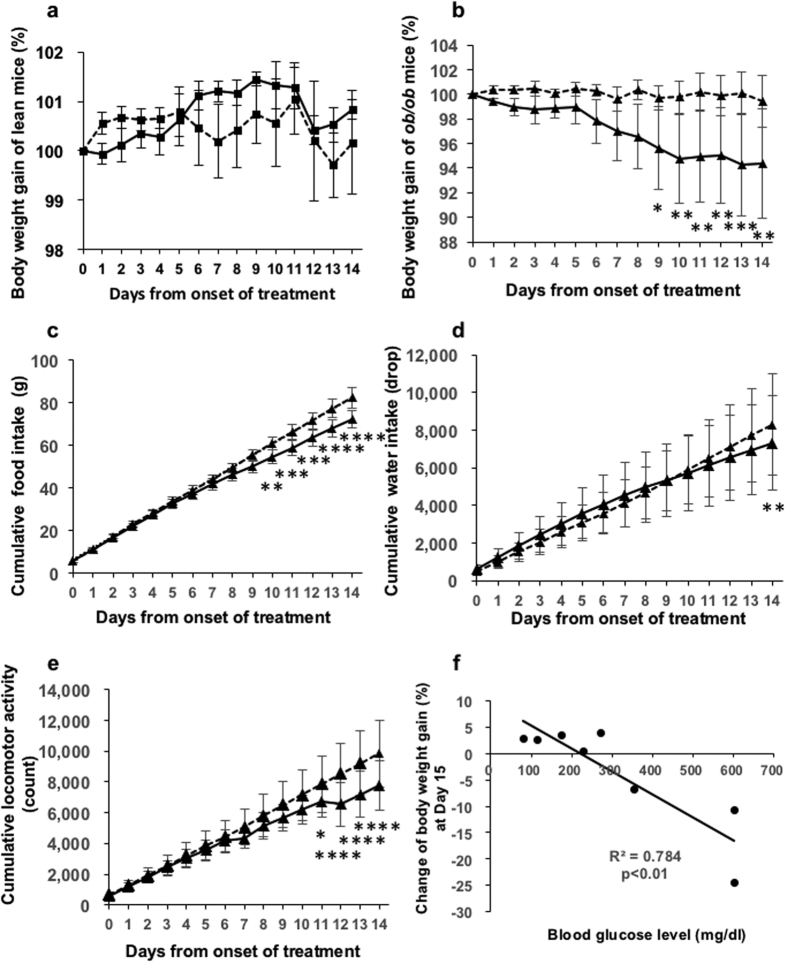
Figure 5. Effect of repeated intranasal GALP treatment in old ob/ob mice.
Effects of repeated intranasal administration of GALP on body weight gain, daily food intake, cumulative water intake and cumulative locomotor activity in lean and ob/ob mice at 20 weeks of age. (a) Body weight gain in lean mice (n = 4). (b) Body weight gain, (c) cumulative food intake, (d) cumulative water intake, and (e) cumulative locomotor activity in ob/ob mice with hyperglycemia (n = 6). The first injection of GALP occurred on day 0. (f) Relationship between body weight gain 24 h after the 14th intranasal administration of GALP and blood glucose level in ob/ob mice with hyperglycemia or normoglycemia (n = 8). The data are expressed as mean ± s.e.m., and analyzed by repeated two-way ANOVA followed by Bonfferoni’s test. The correlation analysis was performed using the Pearson’s product moment correlation coefficient. *p < 0.05 vs. vehicle-treated group; **p < 0.01 vs. vehicle-treated group; **p < 0.001 vs. vehicle-treated group; ****p < 0.0001 vs. vehicle-treated group.