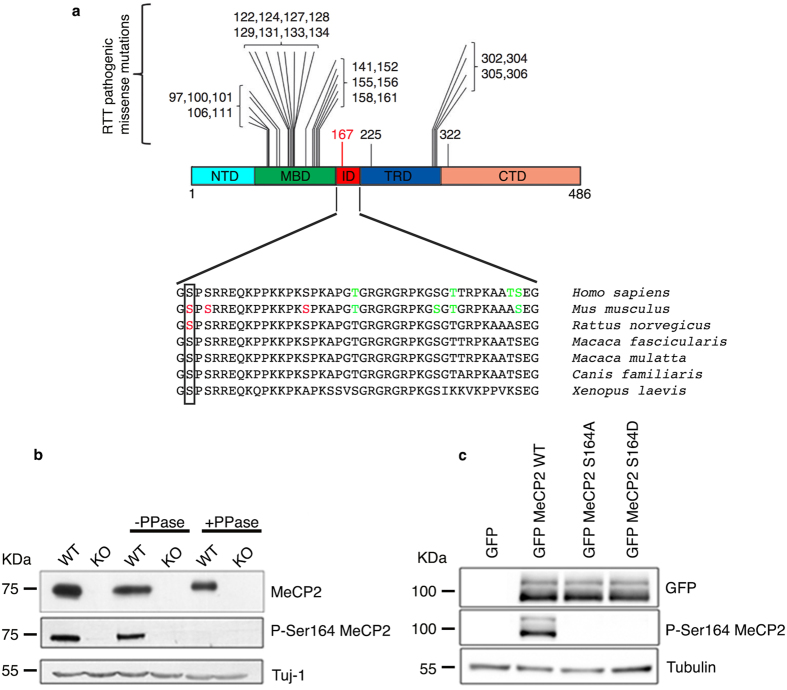
Figure 1. Development of an MeCP2 S164 phospho-specific antibody.
(a) (Adapted from16) Schematic illustration showing the localization of frequent pathogenic missense mutations within MeCP2 domains. The recently identified R167 W pathogenic mutation is indicated in red. Lower part shows alignment of the ID (aa 163–206) from H. sapiens to X. laevis. Box shows the conserved S164. Red residues represent experimentally determined phosphorylated sites; in green are indicated phosphorylated amino acids predicted by GPs 2.0 and NetPhos 2.012. (b) Total brain lysates were prepared from adult WT and KO mice, treated or not with λ phosphatase and analyzed by WB using antibodies against MeCP2 and P-S164 MeCP2. 30 μg of extract were loaded in each lane. Neuronal specific β III tubulin (Tuj1) was used as loading control. (c) Extracts from HEK293T cells expressing GFP-MeCP2 or its S164A and S164D derivatives were analyzed by WB with antibodies against P-S164 MeCP2 or total MeCP2. 20 μg of total lysates were loaded in each lane. Tubulin was used as loading control.