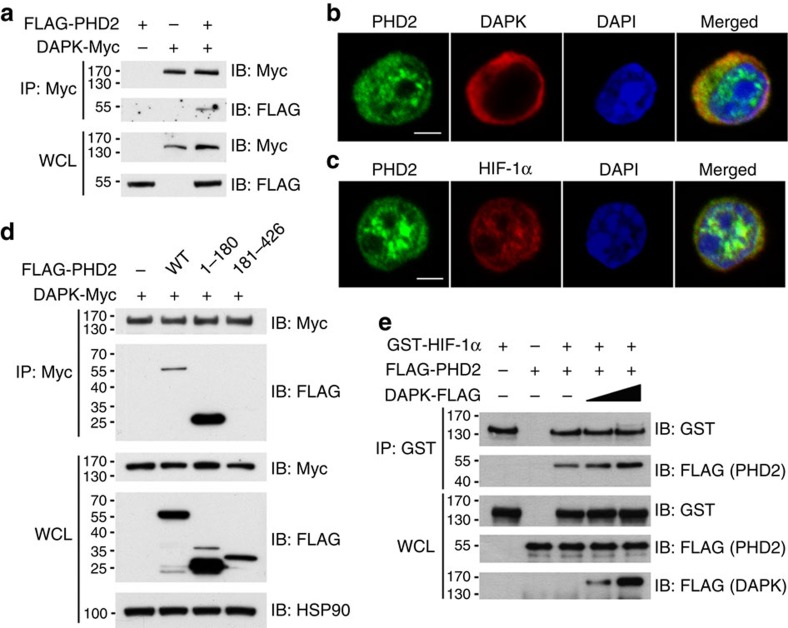
Figure 6. DAPK interacts with PHD2 and increases PHD2-HIF-1α association.
(a) Interaction of DAPK with PHD2. Jurkat cells were transfected with FLAG-PHD2 and DAPK-Myc. The whole-cell lysates (WCL) were immunoprecipitated with anti-Myc, and the contents of FLAG-PHD2 and DAPK-Myc in the precipitates and WCL were determined by anti-FLAG and anti-Myc. (b) Co-localization of DAPK with PHD2 in Th17 cells. WT naive T cells were differentiated into Th17 for 2 days, and cells were fixed. Fixed cells were stained with anti-PHD2, anti-DAPK and DAPI, and analysed by confocal microscopy. Scale bar, 2.5 μm. (c) Co-localization of HIF-1α with PHD2 in Th17 cells. Th17 cells were stained with anti-PHD2, anti-HIF-1α and DAPI, and analysed by confocal microscopy. Scale bar, 2.5 μm. (d) DAPK interacts with the N-terminal domain of PHD2. HEK293T cells were transfected with DAPK-Myc, and the N-terminal (aa 1–180) or C-terminal (aa 181–426) domain of FLAG-PHD2 as indicated. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Myc, and the contents of PHD2 and DAPK were determined. (e) DAPK increases the association of PHD2 with HIF-1α in vitro. Recombinant GST-HIF-1α protein was incubated with FLAG-PHD2 in the absence or presence of recombinant DAPK-FLAG proteins in PBS at 4 °C for 4 h. The GST-HIF-1α complex was pulled down by anti-GST, and the contents of FLAG-PHD2, GST-HIF-1α and DAPK-FLAG in the precipitates and incubation mixtures were determined. Data (a–e) are representative of two independent experiments.