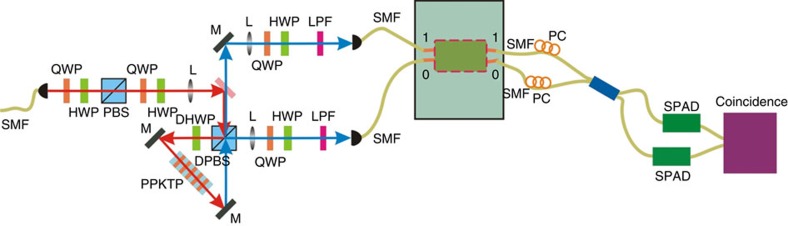
Figure 2. Experimental set-up for the two-photon source and sample measurement.
The continuous-wave pump laser at 779 nm is from a Ti:sapphire laser (Coherent MBR 110). It is collected into single-mode fibre (SMF) before entering the Sagnac-loop. A quarter wave plate (QWP) and a half wave plate (HWP) are used to control the phase and intensity of the pump beams in the Sagnac-loop. In the present experiment, the pump laser with vertical polarization is focused by a lens (L) with a focus length of 200 mm, whose beam waist is ∼40 μm at the centre of the PPKTP crystal. The type II PPKTP (Raicol crystals) crystal has a size of 1 × 2 × 10 mm, with a periodical poling period of 46.2 μm. The temperature of the PPKTP crystal is controlled by a home-made temperature controller with a stability of 2 mK. After a double PBS (DPBS), the polarization of the pump beam is changed to horizontal by a double HWP (DHWP) before the PPKTP crystal. The orthogonal polarized photon pairs generated in the counterclockwise direction are separated by the DPBS and collected into SMFs by using a lens set consisting of two lenses with different focus lengths of 100 and 50 mm at each output port of the DPBS, respectively. The pump beam is removed using a long pass filter (LPF, FELH1400). We use HWPs and QWPs to control the polarizations of the photon pair before injecting into the silicon chip. The output photons from the chip are detected by two InGaAs single-photon avalanche detectors (SPAD, D220, free running single-photon detector), with polarization controlled by fibre polarization controllers (PCs). The grating coupling method is used to couple the single photons into/out of the chip from/into the fibre arrays.