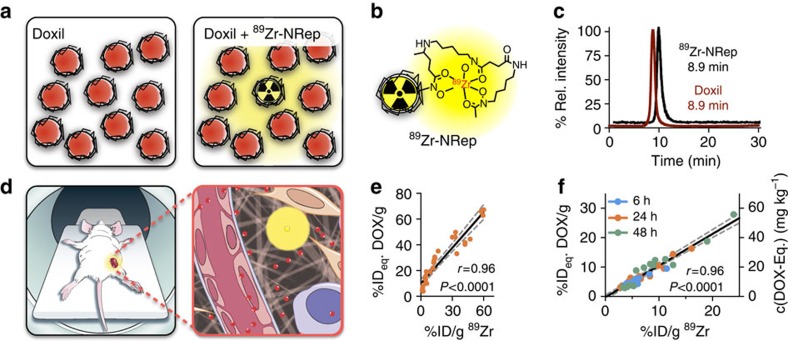
Figure 1. Nanoreporter PET imaging concept.
(a) Schematic representation of the FDA-approved Doxil nanoformulation (left) and the 89Zr-NRep doped Doxil nanoformulation used in this study (right). (b) The liposomal nanoreporter 89Zr-NRep modified with 89Zr-chelating DFO. (c) Compared size exclusion retention times for clinical grade Doxil nanoformulation (fluorescence emission, red) and 89Zr-NRep (HPLC γ-counter, black). (d) Co-injecting 89Zr-NRep and Doxil allows non-invasive quantification of DOX delivery. © 2016, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center. (e) Correlation between 89Zr-NRep (%ID per g) and DOX (%IDeq./g) in blood. Data points (N=28) represent individual blood samples, from which activity was counted (γ-counter) before DOX was extracted and quantified. (f) Correlation between 89Zr-NRep (%ID per g) and DOX (%IDeq./g) uptake. Data points (N=45) represent tumour tissue from mice euthanized at 6 h (blue), 24 h (orange) or 48 h (green) post administration. Tissues were excised, and associated activity counted (γ-counter), before DOX was extracted from the tissues. Pearson's r coefficients were calculated to determine correlation.