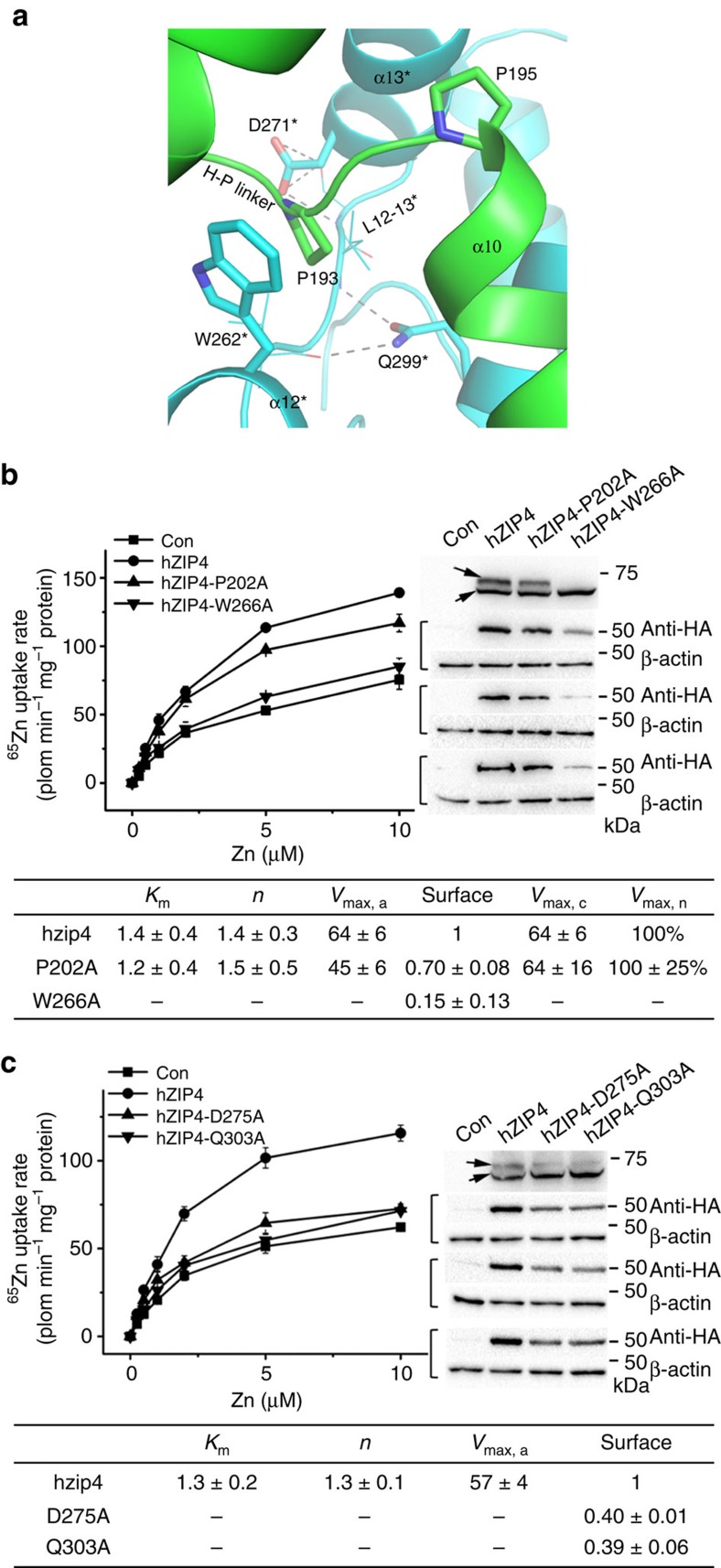
Figure 5. The roles of the bridging region in ZIP4 biogenesis and zinc transport.
(a) The zoomed-in structure of the bridging region. The key residues are shown in stick mode and other involved residues are shown in line mode. The dashed lines indicate potential hydrogen bonds. In hZIP4, P202 (P195 in pZIP4), W266 (W262 in pZIP4), D275 (D271 in pZIP4) and Q303 (Q299 in pZIP4) are mutated into alanine. (b) Functional characterization of P202A and W266A. (c) Functional characterization of D275A and Q303A. In both b and c, the raw experimental data of zinc transport assay (left), and western blots of the mutants in HEK293T cells, surface expression detection and western blots of β-actin (right) are from one representative experiment and the data sets from the other two independent experiments are shown in Supplementary Fig. 8e–h. Zinc transport kinetic parameters and statistical analysis are shown in the tables at the bottom. The units of Km and Vmax are μM and pmol min−1 mg−1, respectively. For W262A, D275A and Q303A, their zinc transport activities are too low to be accurately determined using the current approach. See more detailed data processing in Experimental Procedure and the figure legend of Fig. 1.