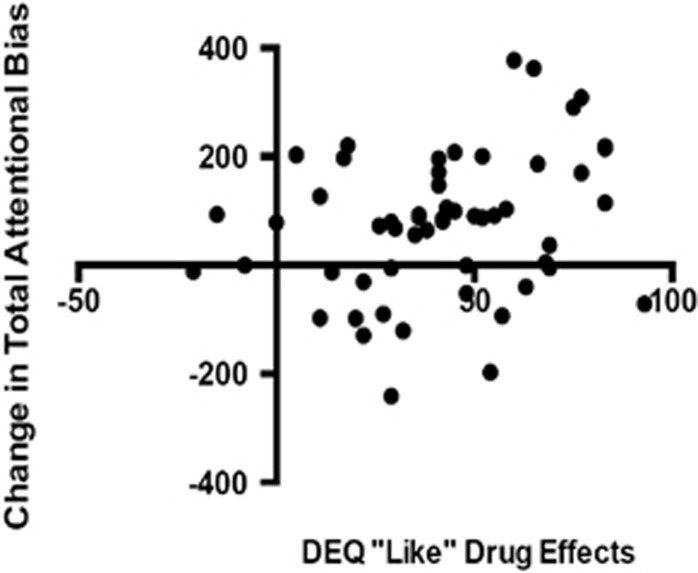
Figure 3.
Individual subjects' ratings of MA liking in relation to their change in attention toward the MA cue. Values shown indicate the change in sustained attention ([sustained attention towards MA cue] minus [sustained attention towards PBO cue]) and subjective “liking” of MA effects (DEQ “Like Drug Effects” mean peak change score at MA session—DEQ “Like Drug Effects” peak change score at PBO session scores) had a positive significant relationship. Subjective ratings of “liking” MA predicted increased attentional bias. Pearson's r=0.28, p=0.019.