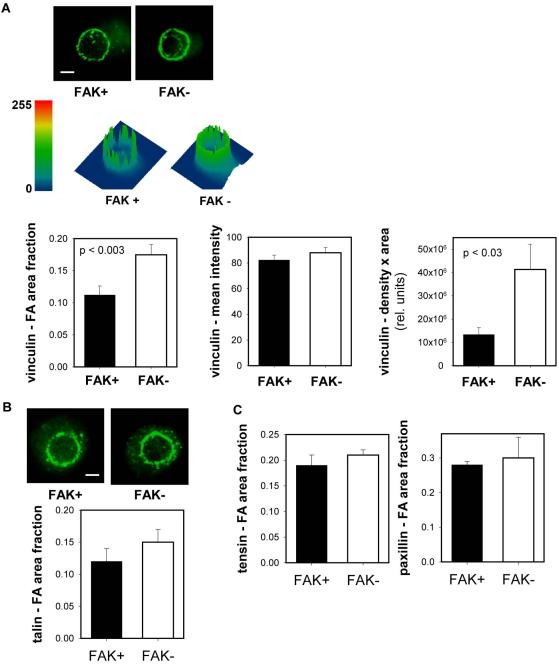
Figure 2.
FAK modulates vinculin localization to the adhesive interface independently from changes in integrin binding. (A) Immunostaining for vinculin recruitment to micropatterned adhesive area showing differences in vinculin-containing focal adhesion area (scale bar, 2 µm). Surface plots displaying vinculin staining intensity (height) and distribution within micropatterned area. FAK+ cells exhibited reduced vinculin-positive area compared to FAK− cells, while vinculin intensity was equivalent for both cell types. Quantification of vinculin-occupied adhesive area, intensity, and area-intensity product. (B,C) Immunostaining (talin) and quantification of focal adhesion components recruited to micropatterned adhesive area showing no differences between FAK+ and FAK− cells.