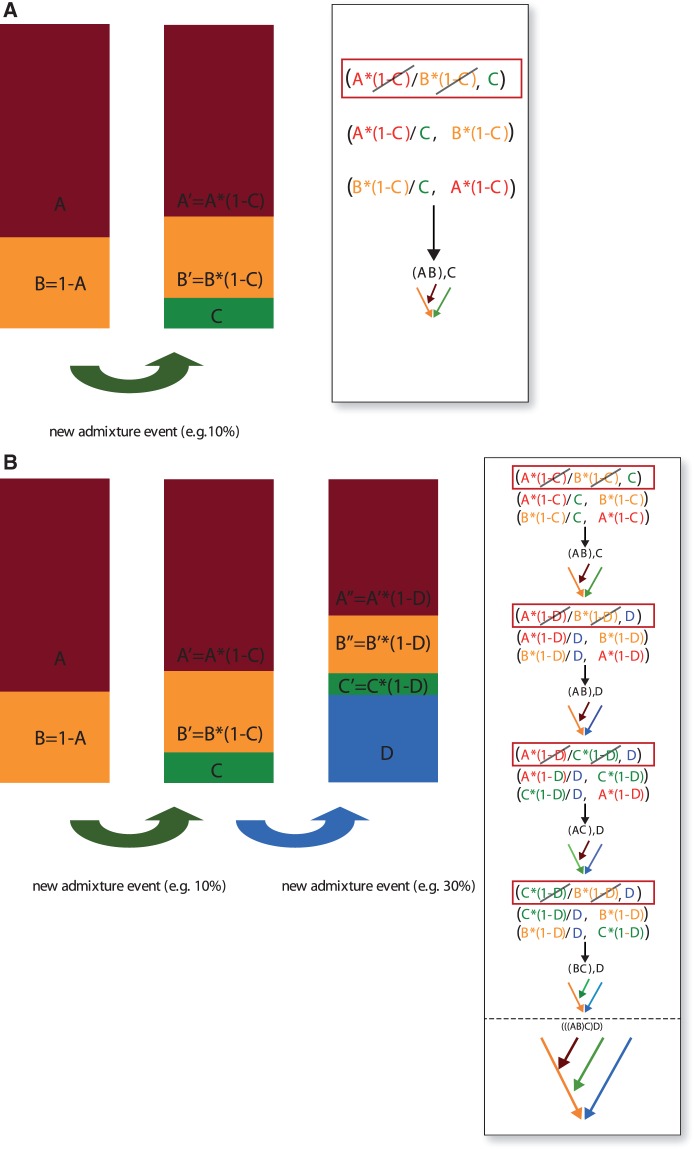
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of the AHG approach. (A) When an already admixed population with ancestry coming from two different sources A and B experiences another episode of admixture, which brings into this population a new ancestry component C, the proportion of ancestry A and B in each individual in this population becomes adjusted by an amount which depends on the proportion of the component C in the individual. Although before the admixture episode the proportion of A and B among the individuals in the population varied independently of each other, after the new admixture episode A and B start to covary because due to the influx of C each of them has been adjusted by the same amount. The test is based on the detection of this covariance between A and B, as is further illustrated in the inset. (B) An example involving additional gene flow from ancestry D.