Figure 5.
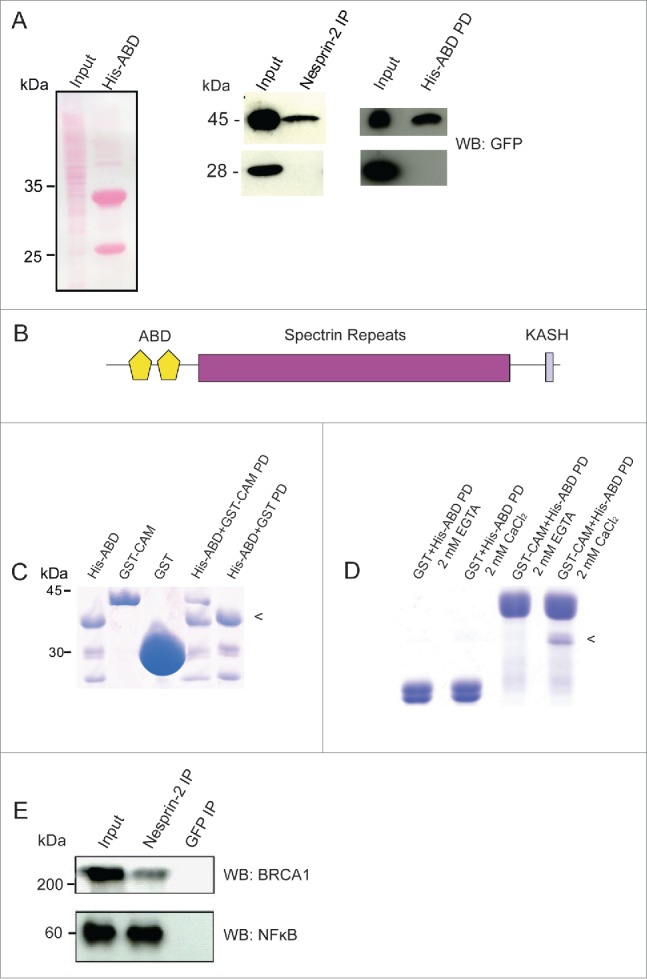
Nesprin-2 interacts with Calmodulin, BRCA1 and NF-κB. (A) Left panel, Ponceau S stained gel showing the HaCaT cell lysate (Input) used for pull down and immunoprecipitation and the His-ABD polypeptide (~33 kDa). The smaller band at ~25 kDa is presumably a breakdown product. Middle panel, detection of YFP-Calmodulin (45 kDa) in the Nesprin-2 immunoprecipitate (IP) using pAbK1. Right panel, detection of YFP-Calmodulin in the His-ABD pull down (PD). The panels below show the control pulldowns with cells expressing YFP (28 kDa). Detection was with mAb K3–184–2. (B) Domain structure of Nesprin-2 showing the localization of the ABD composed of 2 CH domains, the rod domain made from spectrin repeats and the C-terminal KASH domain which harbors a transmembrane domain. (C) Direct interaction of the Nesprin-2 ABD and Calmodulin. His-ABD bound to Ni-NTA beads was incubated with GST-Calmodulin (GST-CAM) or GST for control. PD, pull down. (D) For analyzing the Ca2+ dependence of the interaction, His-ABD released from beads was incubated with GST-calmodulin bound to beads in the presence of Ca2+ or its absence (+EGTA). The arrowhead in (C) and (D) points to the position of His-ABD. (E) Coimmunoprecipitation of BRCA1 and NF-κB from HaCaT cell lysates (Input) with Nesprin-2 antibodies pAbK1 (IP). mAb K3–184–2 against GFP was used for control. The resulting blots were probed with BRCA1 and NFκB specific antibodies, respectively.
