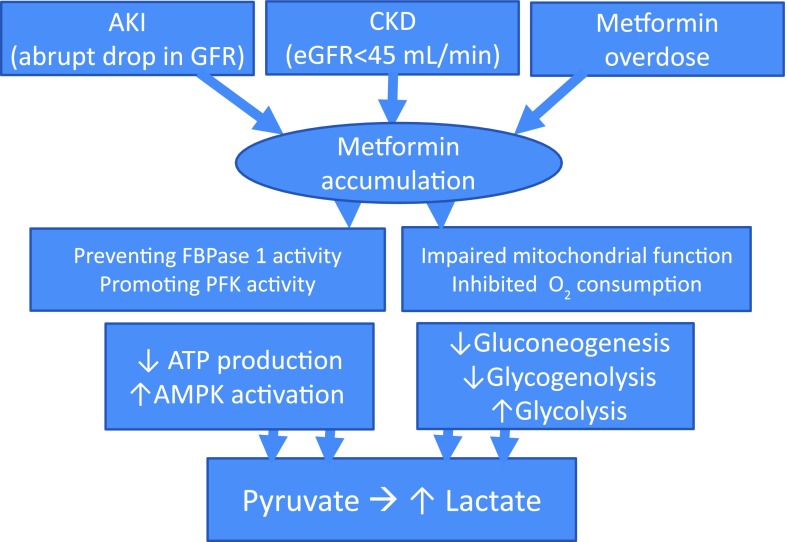
Figure 1.
Putative mechanisms of lactic acidosis with use of metformin under renal impairment. Biguanides, including metformin, may be accumulated with acute worsening of kidney function or upon gradual progression of CKD. The resultant increase in PFK activity along with FBPase 1 activity inhibition suppresses gluconeogenesis and stimulates glycolysis. The subsequent decrease in hepatic energy status activates AMPK, a cellular metabolic sensor, leading to a reduction in hepatic gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis while glycolysis is promoted and enhanced by impaired mitochondrial function with secondary inhibition of oxygen consumption, resulting in increased lactate generation and accumulation. FBPase 1, fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase 1; PFK, phosphorylated phosphofructokinase 2.