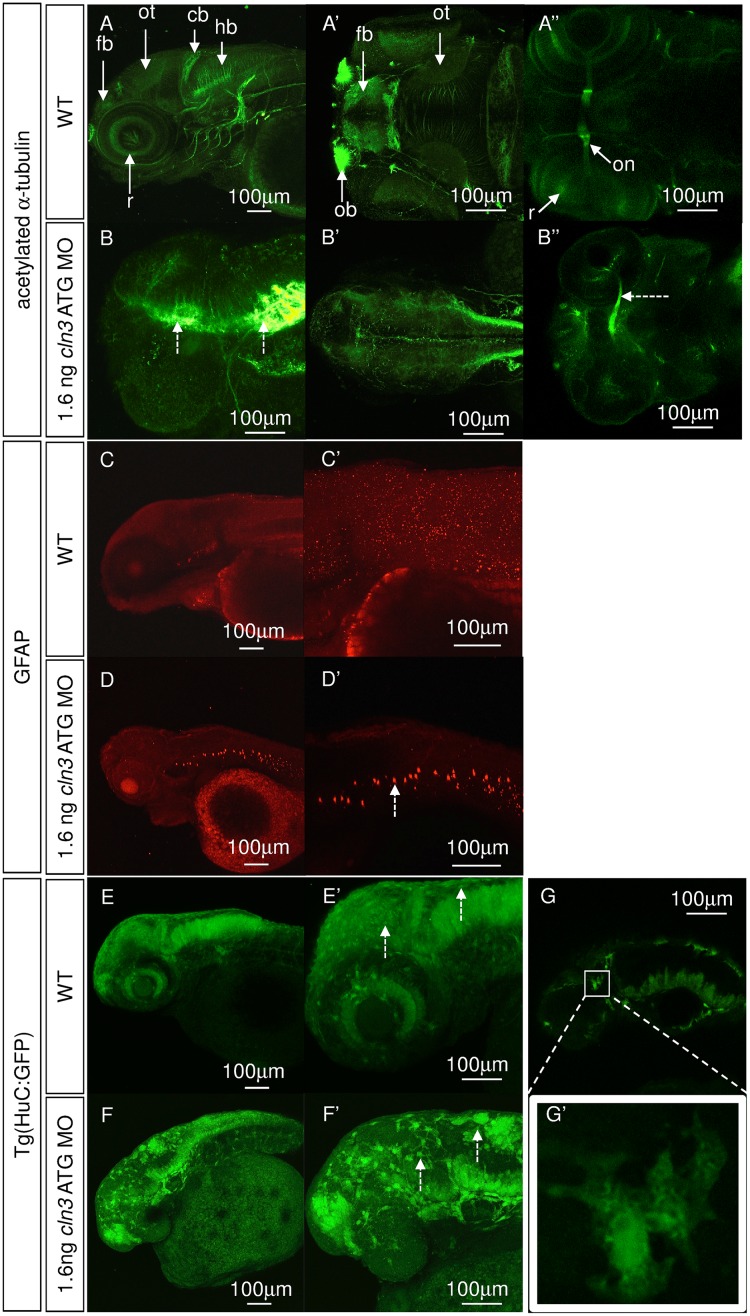
Fig 6. Neurons and glia are disrupted in cln3 ATG MO morphants.
(A-A”, B-B”) Immunohistochemical staining for axons (acetylated α-tubulin) at 4 dpf. (A-A”) normal development of axons in WT larvae. (B-B”) 1.6 ng cln3 ATG MO morphants have a complete absence of axonal organisation throughout the brain, with axonal accumulation (B, dashed arrows), loss of the optic tectum and a narrowing of the optic nerve (B'', dashed arrow). (A-A”, B-B”), anterior to the left; A, B, lateral view, dorsal up; A’, B’, dorsal view; A”, B” ventral view. (C-C’, D-D’) Immunohistochemistry using antibodies to glia (glial fibrillary acidic protein, GFAP) at 4 dpf. (C-C”) Normal staining in WT larvae. (D-D’) Ectopic GFAP is observed in the notochord in 1.6 ng cln3 ATG MO morphants (dashed arrow). Lateral view. Anterior to the left. Dorsal up. (E-E’, F-F’, G-G’) Transgenic zebrafish expressing GFP under the control of the HuC promoter in neurons were injected with 1.6 ng cln3 ATG MO and observed at 3 dpf. (E-E’) In WT zebrafish, the normal structure of the developing brain and retina can be observed. (F-F’) In morphants, there appear to be fewer neurons and the normal brain structure is lost. Many GFP-positive cells were enlarged and found nearer the surface of the brain (F’, dashed arrows). (G-G’) When the morphology of these enlarged cells was examined further, they lacked typical neuronal morphology. Lateral view. Anterior to the left. Dorsal up. Abbreviations: cb, cerebellum, fb, forebrain; hb, hindbrain; ot, optic tectum; on, optic nerve. A-G” (all images) Z projection. Scale bars: 100 μm. n = 4 per group.