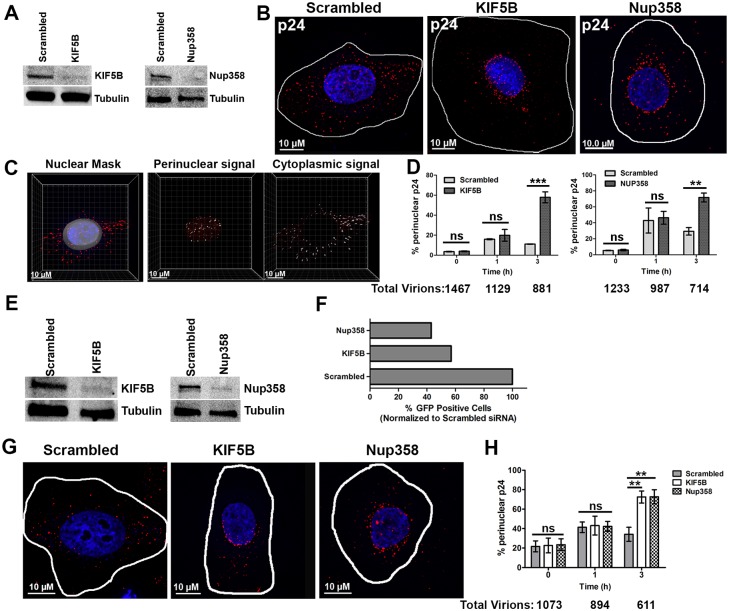
Fig 2. KIF5Band Nup358 depletion lead to the perinuclear accumulation of HIV-1 cores.
HeLa cells were transfected with siRNA’s targeting Nup358, KIF5B or a scrambled siRNA sequence.(A) Western blot for KIF5B or NUP358 96h following siRNA transfection (B)siRNA depleted cells were synchronously infected withVSVg-R7ΔEnvGFP(MOI 0.6). Cells were fixed 0, 1and 3h following a synchronized infection and stained for HIV-1 capsid protein p24 (red) and DAPI (blue) for cell nuclei. A representative image at 3h post infection is depicted.(C)Quantification process employed to detect perinuclear and cytoplasmic p24 protein levels. Nuclear mask generated based on the DAPI channel (left image) and perinuclear signal quantified by masking all signal inside (middle image) or outside right image) of the nuclear mask. (D)Percentage ofp24 puncta in the perinuclear region in KIF5B and Nup358 depleted cells, quantified as described in (C). TZM-bl cells were transfected with siRNA’s targeting Nup358, KIF5B or a scrambled siRNA sequence.(E) Western blot for KIF5B or NUP358 72h following siRNA transfection. siRNA depleted cells were synchronously infected with HXB2-R7ΔEnvGFP(MOI 0.32). (F)Infectivity was assessed 48 hours following infection. (G,H) Cells were fixed 0, 1and 3h following a synchronized infection and stained for HIV-1 capsid protein p24 (red) and DAPI (blue) for cell nuclei. A representative image at 3h post infection is depicted. (H) Percentage ofp24 puncta in the perinuclear region in KIF5B and Nup358 depleted cells, quantified as described in (C). 20 or more cells was analyzed at each time point. Error bars represent the SEM of three experiments. The total number of virions analyzed at each time point is shown below each graph. ***p<0.001, *p<0.05, ns = not significant. Data is representative of three or more independent experiments.