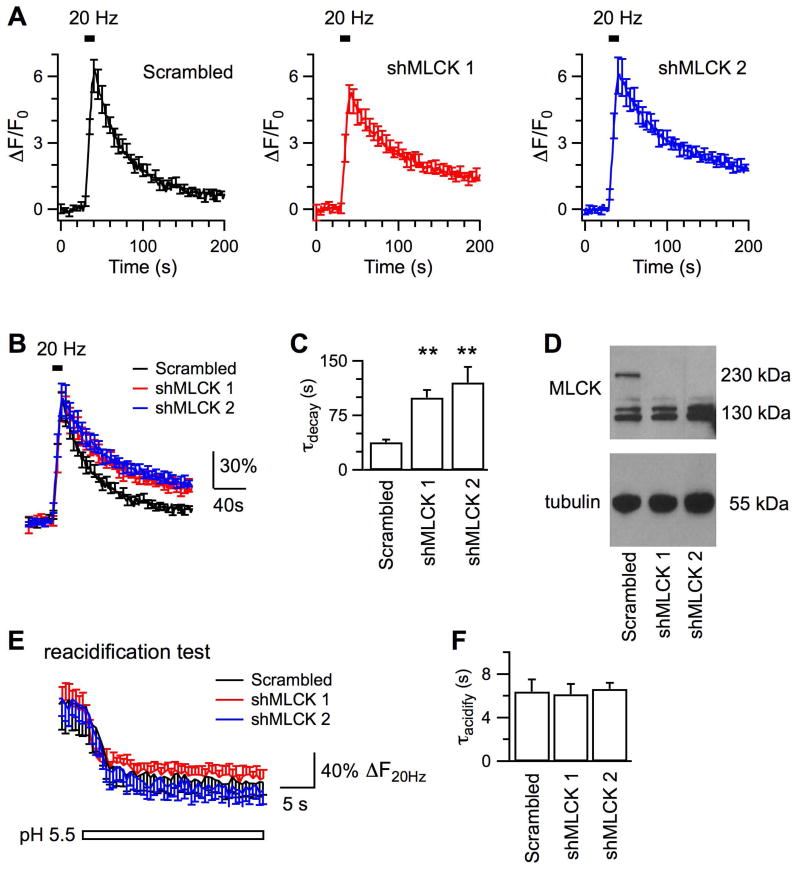
Figure 3. Genetic downregulation of endogenous MLCK impairs endocytosis induced by action potentials at 20 Hz.
A, Averaged changes of SypHy fluorescence induced by 200 action potentials delivered at 20 Hz from hippocampal boutons transfected with the scrambled shRNA (Scrambled, Nexp = 9), shMLCK 1 (Nexp = 6) and shMLCK 2 (Nexp = 8), respectively. B, Averaged fluorescence traces after normalization to the peak ΔF induced by action potentials. C, Comparison of endocytosis kinetics. D, Immunoblotting results showing that transfection with shMLCK 1 or shMLCK 2, but not the scrambled shRNA, decreased the level of endogenous MLCK in hippocampal neurons. E, Averaged changes of SypHy fluorescence in tests to measure vesicle reacidification, same as in Fig.2B. Boutons had been transfected with the scrambled shRNA (Nexp = 5), shMLCK 1 (Nexp = 6) and shMLCK 2 (Nexp = 8), respectively. The similar decay kinetics of the stimulated fluorescence in pH 5.5 suggests that down-regulation of MLCK does not affect vesicle reacidification. F, Time constants of vesicle reacidification from boutons transfected with either the scrambled shRNA or a shMLCK to down-regulate the endogenous MLCK.