Figure 7. Putative pro-life pathway(s) induced by quercetin.
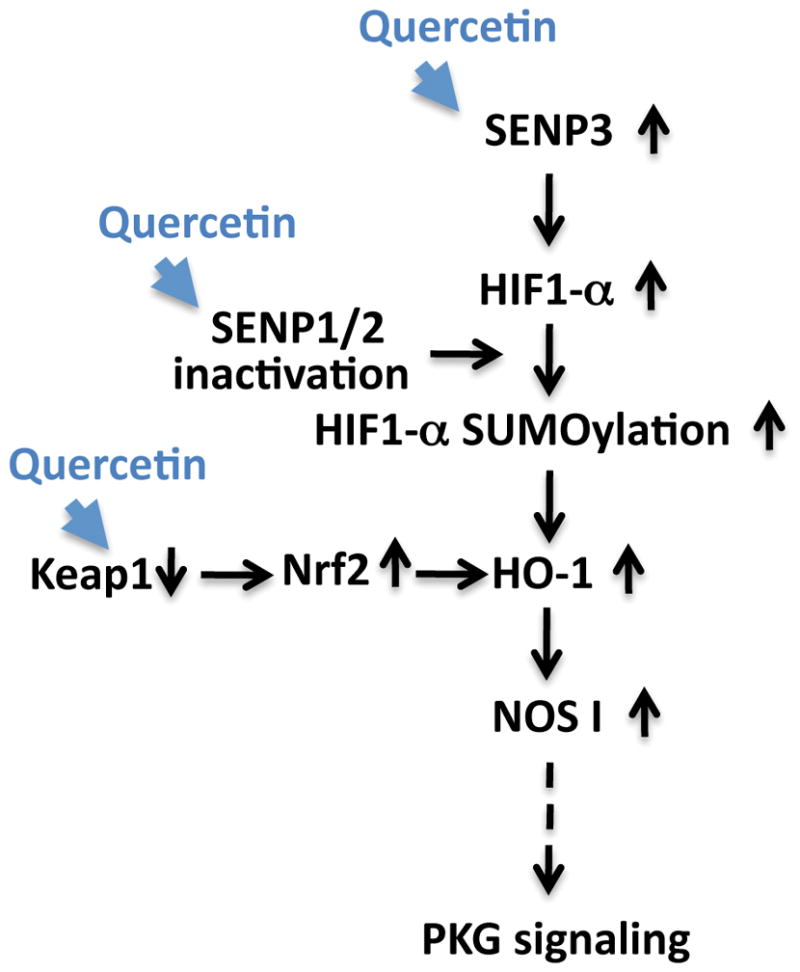
Quercetin acts to increase survival in the face of ischemia via an increase of SENP3 expression, the possible inactivation of SENPs 1/2, and via a decrease in KEAP1 levels (thereby increasing Nrf2 stability). These changes may then lead to increase in HIF-1α SUMOylation and HO-1 activation, followed by an upregulation of NOS1/PKG signaling. Pathways altered via quercetin treatment within our experimental system are represented by blue arrowheads. Solid black arrows represent relationships that have been explored while a dotted arrow represents a relationship that has yet to be confirmed.
