FIGURE 4.
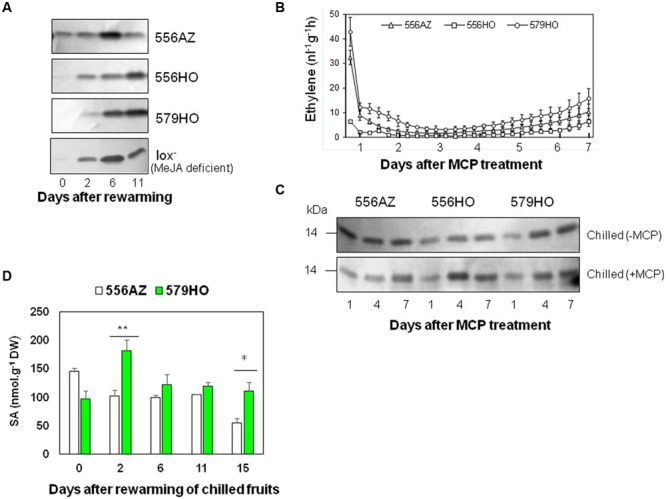
(A) Accumulation of PR1b1 protein in methyl jasmonate-deficient (lox-) fruit in comparison to azygous control (556AZ) and SAMdc transgenic (556HO, 579HO) fruits upon chilling and re-warming. (B,C) Effect of MCP treatment of fruits from the different lines on ethylene production (B), and PR1b1 protein accumulation (C). The fruits, immediately after chilling were treated with 5 ppm MCP for 24 h at 20°C and analyzed for: (B) Rate of ethylene production measured at intervals during the course of 7 days (bars represent standard error of means; n = 4); (C) accumulation of PR1b1 protein in MCP-treated (+MCP) and control (–MCP) fruits. PR1b1 accumulation was determined by immunoblotting using anti PR1abc antibody. (D) Salicylic acid (SA) levels in azygous control (556AZ) and SAMdc transgenic (579HO) fruits. The fruits were chilled and re-warmed as described in the legend to Figure 1. Statistically significant values of SA between 566AZ and 579HO at the specified days after rewarming of chilled fruits are marked on the bars with ∗ (P < 0.08) and ∗∗ (P < 0.05).
