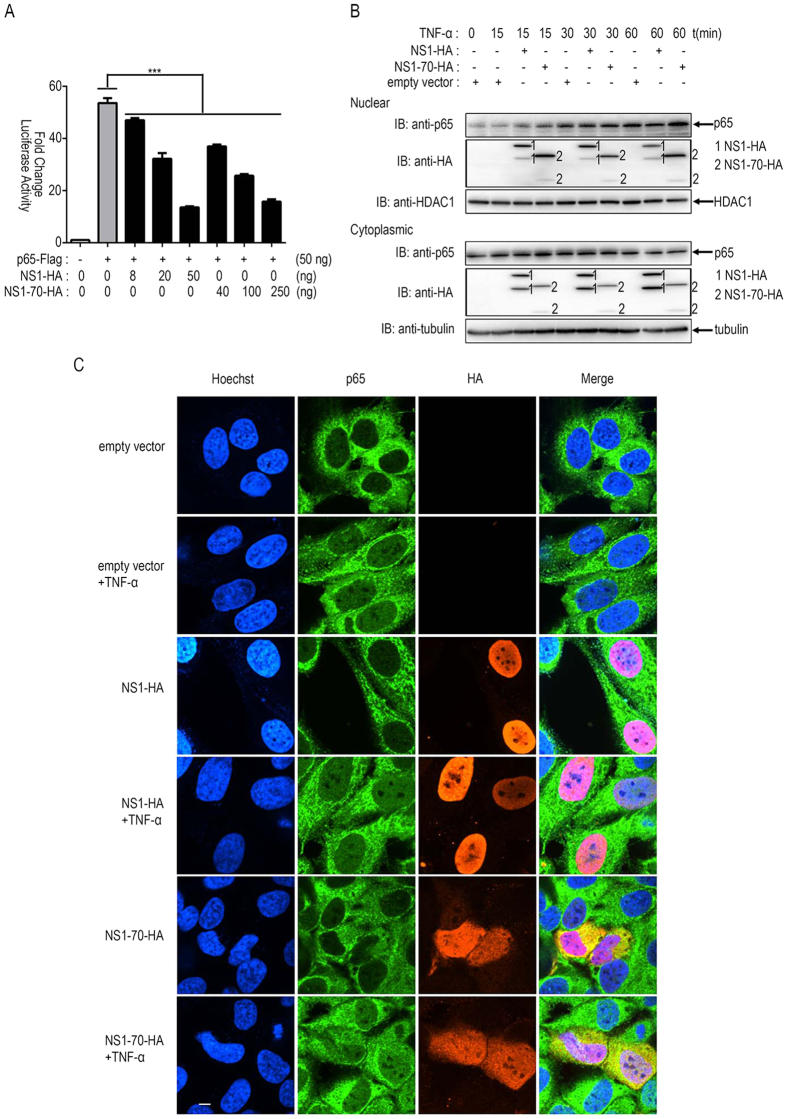
Figure 4. HBoV NS1 and NS1-70 do not block p65 nuclear translocation.
(A) 293T cells in 24-well plates were cotransfected with 125 ng of pNF-κB-luc, 25 ng of pRL-TK, and FLAG-p65 together with specific amounts of NS1 or NS1-70 expression plasmids. Total amounts of transfected DNA were kept equal by adding an empty vector. Reporter activity was determined 30 h post-transfection by dual-luciferase reporter assays. The resultant ratios were normalized to the fold-change values by that of TNF-α-untreated cells cotransfected with empty vectors, pNF-κB-luc and pRL-TK. Data represent at least 3 independent experiments, with each determination performed in duplicate (mean ± SD of fold-change). Asterisks indicate significant differences between groups (***p < 0.01, Student’s t-test). (B) 293T cells were transfected with NS1, NS1-70 expression plasmid, or empty vector for 30 h and then mock-treated or treated with TNF-α (10 ng/ml) for 15, 30, or 60 min. Equal amounts of cytoplasmic and nuclear extracts were resolved by immunoblotting with the anti-p65 antibody or the anti-HA antibody. HDAC1 and tubulin were used as loading controls for nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins, respectively. (C) HeLa cells were transfected with NS1, NS1-70 expression plasmid, or empty vector for 30 h. The cells were then mock-treated or treated with TNF-α (10 ng/ml) for 30 min. HeLa cells were subjected to immunofluorescence staining for detection of p65 subcellular localization by using rabbit anti–p65 and FITC-conjugated secondary Ab (green). NS1 and NS1-70 expression levels were detected using a mouse anti-HA tag and Texas Red-conjugated secondary Ab (red). Nuclei were stained by Hoechst 33258 (blue). One of three experiments is shown.