Figure 2.
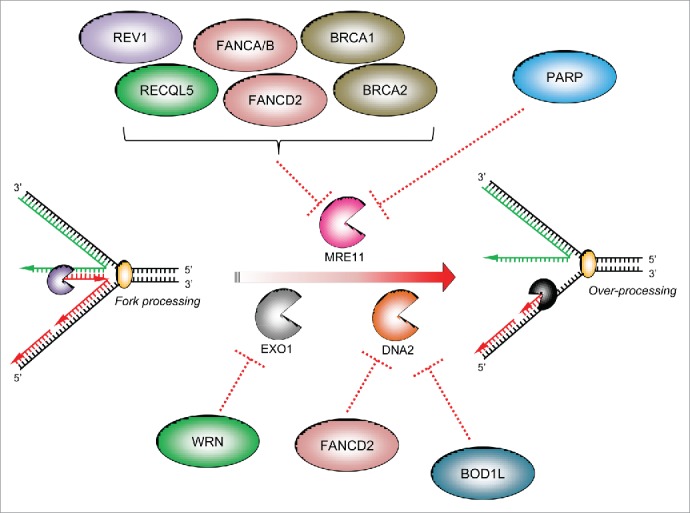
The specificity of factors counteracting ‘fork’ nucleases: Three main cellular nucleases have thus far been implicated in the over-processing of stalled forks: MRE11, DNA2 and EXO1. There have been no reports that the nuclease CtIP is involved in over-processing of stalled replication forks. Several protective factors act on specific cellular nucleases to supress their aberrant activity on stalled replication forks (dotted red lines): several FA/HR proteins, the TLS polymerase REV1 and PARP1 have all been reported to inhibit MRE11-dependent fork resection, whilst the WRN helicase/nuclease prevents EXO1-dependent fork degradation. Recently, we demonstrated that BOD1L is required to suppress DNA2-dependent strand degradation of stalled replication forks, alongside speculative reports of a similar role for FANCD2.
