Figure 1.
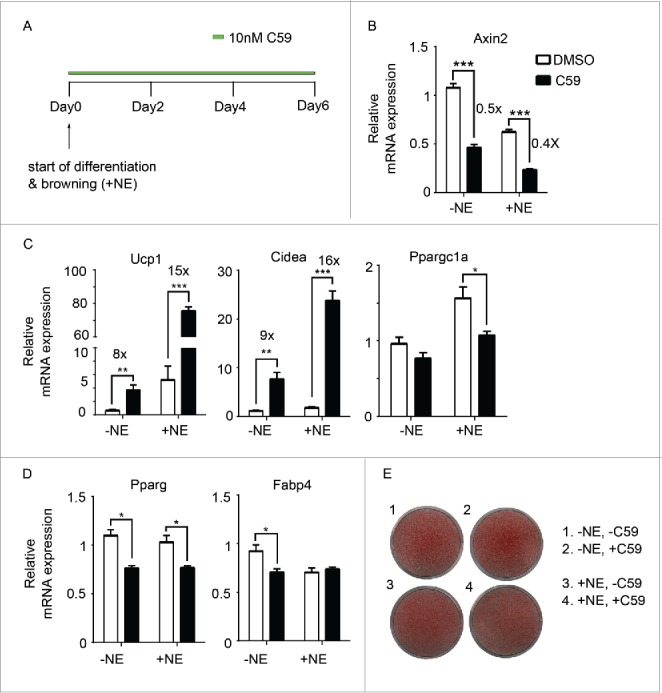
Inhibition of Wnt signaling pharmacologically enhances browning (A) Experiment schematics of in vitro browning experiment. Primary mouse adipocytes differentiated from the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of inguinal fat pads were treated with 10 nM of C59 for 6 d from the start of differentiation. Browning was induced by adding 1 µM norepinephrine. (B-D) qPCR analysis of Wnt signaling gene (Axin2) (B), BAT genes (Ucp1, Cidea, Ppargc1a) (C), and pan-adipocyte genes (Pparg, Fabp4) (D) on RNA extracted at Day 6 according to scheme 1(A). Shown is the relative mRNA expression values normalized with the housekeeping gene Rpl23. All data are presented as mean ± SEM by Student's t-test. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 and *** p < 0.001 comparing with control. The fold of induction or inhibition is indicated when the change is significant and relevant. (E) Oil red O staining of primary mouse adipocytes at Day 6.
