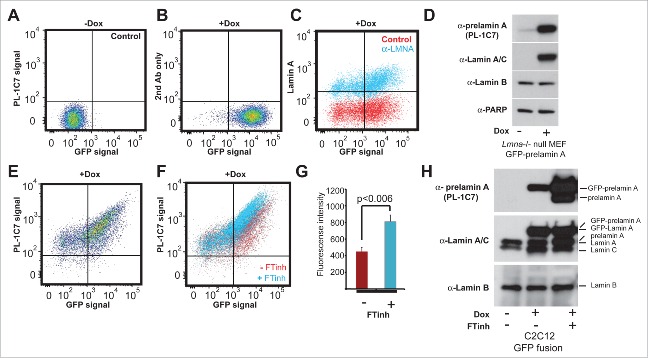
Figure 2.
Quantitative detection of prelamin A by intracellular flow cytometry (IFC). Prelamin A is detected by PL-1C7 antibody in Lmna−/− MEFs stably transfected with Doxycycline (Dox)-inducible GFP-Lmna transgene using IFC. (A). Control, non-induced GFP-Lmna MEFs (“x” axis, GFP-fusion; “y” axis, prelamin A signal detected using PL-1C7 antibody). (B). Control GFP-Lmna MEFs after 24 hr Dox treatment stained with secondary antibody only (No PL-1C7). (C). Detection of both precursor and processed Lmna gene products (lamin A) with anti-lamin A/C antibody in GFP-Lmna MEFs after 24 hr Dox treatment. (D). Western blot analysis of GFP-Lmna MEF cells treated with Dox for 24h. GFP signal is present on mature lamin A as well as prelamin A. Prelamin A accumulation was detected using the PL-1C7 antibody. Antibodies against lamin A/C, lamin B and PARP1 were used as controls. (E). Dox-treated GFP-Lmna MEF stained with PL-1C7 antibody (prelamin A). (F). Farnesyl transferase inhibitor (FTinh) induced prelamin A accumulation in GFP-Lmna MEFs detected by IFC using the PL-1C7 antibody (G). Fluorescence geometric median of prelamin A detection using PL-1C7 by IFC after FTihn treatment of GFP-Lmna MEFs. (H). Western blot analysis to detect prelamin A accumulation in Dox induced GFP-Lmna C2C12 myoblasts upon FTinh treatment. Antibodies against lamin A/C and lamin B were used as controls. See also Fig. S2.