Figure 1.
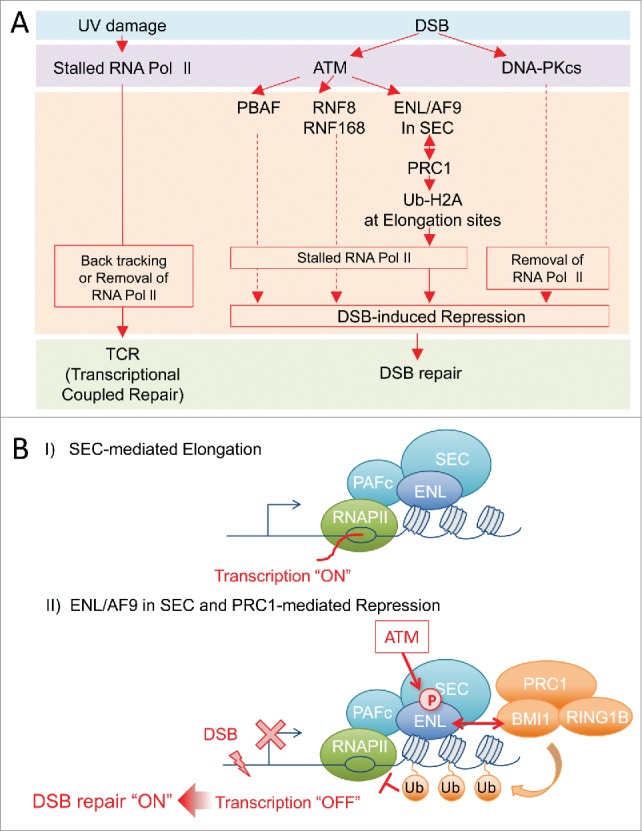
(A) Link between DNA damage and transcription, and pathway of DSB-induced transcriptional repression. (Left) UV damage-stalled RNA Polymerase II recruits NER proteins and induces transcription coupled repair (TCR). (Right) DSBs activate ATM and/or DNA-PKcs and promote DSB-induced transcriptional repression and DSB repair. Under the ATM-signaling, PBAF, RNF8/RNF168 and ENL/PRC1 were reportedly involved in DSB-induced transcriptional repression. (B) Models of collaboration between ENL/AF9 and PRC1 in DSB-induced transcriptional repression. I) During transcriptional activation, ENL/AF9 in SEC promotes transcriptional elongation. II) When DSB(s) is introduced near transcriptional sites, ATM phosphorylates ENL/AF9 at evolutionarily well-conserved SQ-sites. This phosphorylation of ENL/AF9 recruits PRC1 at transcription-sites through BMI1 to promote ubiquitination of H2A and transcriptional repression. Thus, ENL/AF9 in SEC would be key factors for the switch of transcriptional elongation to rapid repression, in response to cellular signaling. Dot-line indicates that it is not clear how these factors repress transcription.
