Figure 2.
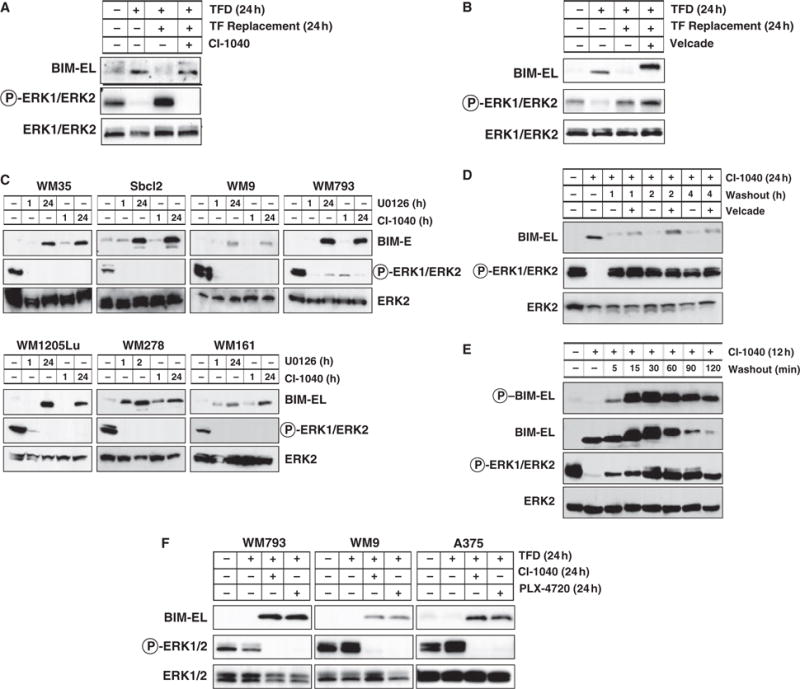
Regulation of BIM expression in human melanocytes and melanoma cells. (A, B) Asynchronously growing primary human melanocytes were subjected to 24 h of TFD. These cells were then re-stimulated with full media containing serum and growth factors for 24 h in the absence or presence of 2 μM CI-1040 or 15 nM Velcade. The phosphorylation and expression of BIM-EL and ERK1/2 were assessed by Western blotting. (C) A panel of human melanoma cells (for details of each cell line visit http://www.wistar.org/herlyn/melanoma.htm) was treated with either 10 μM U0126 or 2 μM CI-1040 to inhibit MEK1/2 for 1 or 24 h as indicated. Cell extracts were then analyzed for BIM-EL expression and phosphorylation and expression of ERK1/2. (D) Asynchronously growing WM793 cells were treated with 2 μM CI-1040 for 24 h. Cells were then cultured in the absence (washout) of 2 μM CI-1040 for 1, 2 or 4 h in the absence or presence of 15 nM Velcade as indicated. Cell extracts were analyzed by Western blotting. (E) Asynchronously growing WM793 cells were treated with 2 μM CI-1040 for 12 h. Cells were then cultured in the absence (washout) of 2 μM CI-1040 for 120 min. Cell extracts were analyzed by Western blotting for Bim-EL expression and serine 69 phosphorylation, and expression and phosphorylation of ERK1/2. (F) Human WM793, WM9 melanoma cells (all expressing BRAFV600E) were subjected to 24 h TFD in the absence or presence of either 2 μM CI-1040 or 10 μM PLX4720. Cell extracts were then analyzed for BIM-EL expression and phosphorylation and expression of ERK1/2.
