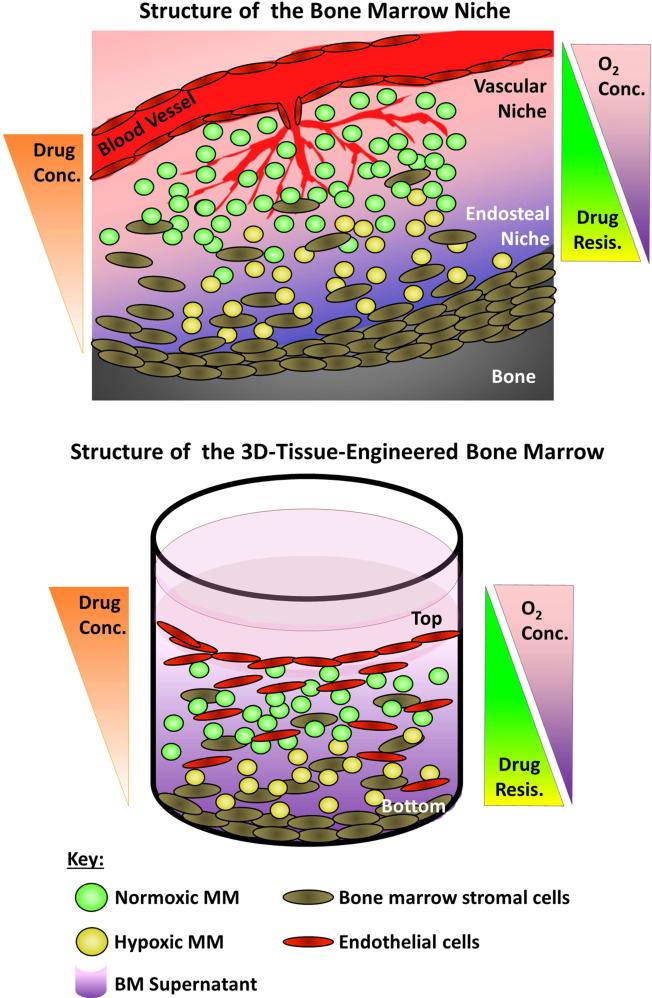
Figure 6. The 3DTEBM recapitulates the BM niche structure.
A) Cartoon of the BM niche with oxygen and drug concentration gradients as a function of the distance from blood vessels. The vascular niche (close to the blood vessels) provides higher levels of oxygenation and contains higher proliferating and more sensitive cells to therapy (green). The endosteal niche (close to the bone) is hypoxic, receives lower effective drug concentrations, and consists of less proliferative and more drug-resistant cells (yellow). B) Cartoon of the three-dimensional tissue engineered BM (3DTEBM) niche with oxygen and drug concentration gradients as a function of scaffold depth. The top of the 3DTEBM is enriched for endothelital cells, where MM cells are exposed to higher oxygen levels and drug concentrations, with more proliferative cells (green). The bottom of the 3DTEBM is hypoxic, receives lower concentration of drugs, and includes less proliferative and more drug-resistant cells (yellow). The 3DTEBM provides a tool for further studying the vascular and endosteal niches in ex-vivo experiments.