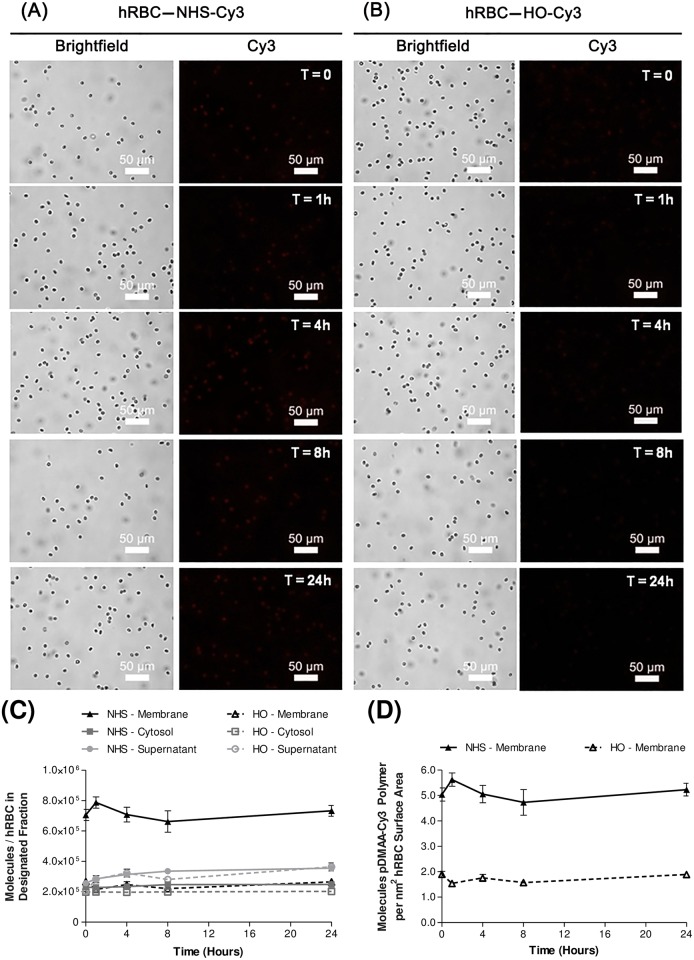
Fig 3. Human erythrocyte membrane engineering with NHS-pDMAA-Cy3 polymers.
NHS-pDMAA-Cy3 polymers are retained on hRBC membranes over a 24 hour period compared to HO-pDMAA-Cy3 polymers, indicating cell surface reactivity. Human RBCs were modified with 100 μM NHS-pDMAA-Cy3 or HO-pDMAA-Cy3 for 30 minutes at 37°C. (A) Representative images of NHS-pDMAA-Cy3-exposed hRBC for each designated time point. (B) Representative images of HO-pDMAA-Cy3-exposed hRBC for each designated time point. Epifluorescent images were capture after washing on a Leica inverted microscope at 40X. Scale bars measure 50 μm. (C) Supernatant, cytosolic, and membrane fractions were collected at 0, 1, 4, 8, and 24 hours. Polymer retention and internalization was assessed by monitoring the relative fluorescence of each fraction over time and calculated as the number of polymer molecules per hRBC using a standard curve. (D) The number of polymer molecules per nm2 hRBC surface area was calculated using an average hRBC surface area of 140 μm2. Images were background corrected and the brightness/contrast for each channel was balanced using Image J software. n = 3.