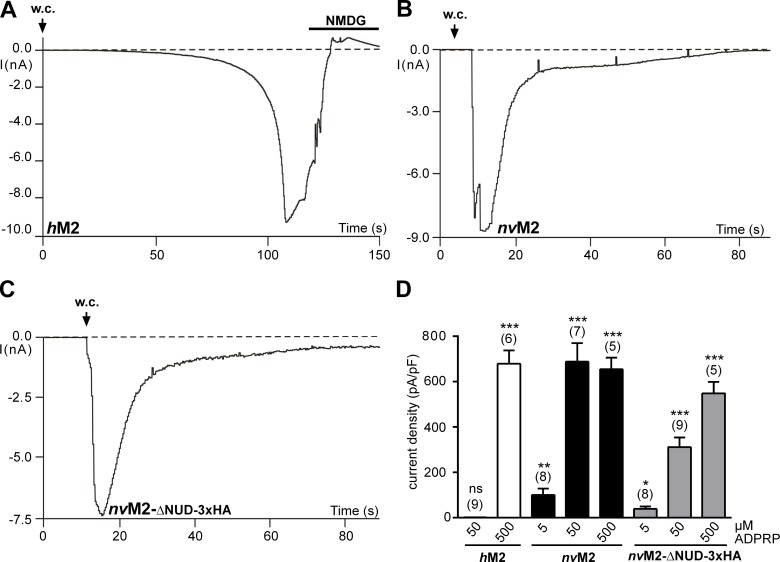
Fig 5. Effects of ADPR-2’-phosphate (ADPRP) on channel variants of hTRPM2 and nvTRPM2.
(A-C) Representative patch-clamp experiments either on wild-type hTRPM2, wild-type nvTRPM2 or nvTRPM2- Δ NUD-3xHA as indicated. Stimulation was performed with 0.5 mM (A) or 50 μM (B and C) ADPRP in the pipette solution. The intracellular Ca2+ concentration was adjusted to 1 μM. The respective current characteristics are indistinguishable from those evoked with ADPR as stimulus. (D) Comparison of the effects of different ADPRP concentrations on each channel variant. Note that 50 μM ADPRP failed to stimulate currents in hTRPM2, whereas in both nvTRPM2 variants significant responses were detected already at 5 μM. Asterisks indicate significant differences (* P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001; Student's t-test, n = 5–9) in comparison to the absence of a stimulus. Error bars are s.e.