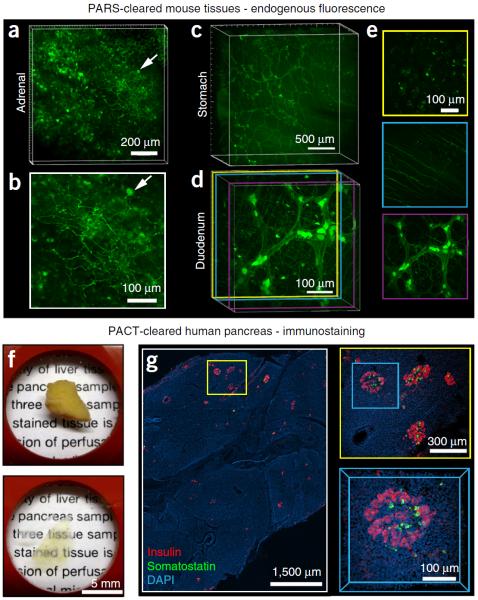
Figure 1.
Applications of whole-organ and whole-organism clearing protocols. (a–e) PARS-based whole-body clearing for assessing cellular-level adeno-associated virus (AAV) tropism (Supplementary Methods). Three weeks after systemic injection of AAV9:CAG-GFP, mice were PARS-cleared and their organs were excised and sectioned for imaging. (a,b) Projection images show GFP+ transduced cells in the adrenal gland. Arrow highlights a GFP+ cell near the surface of the adrenal gland with neuronal morphology, which is shown in higher magnification in b. (c) Projection images show GFP+ cells in the stomach from the surface to the lumen. GFP expression is particularly high in the myenteric plexus. (d,e) AAV9 transduces cells in several layers within the intestine (duodenum). (d) Projection image of GFP fluorescence. Double colored lines correspond to the positions of 50-μm maximum projection images extracted from the data set and presented in e. (e) GFP+ cells in the intestinal crypt (top), submucosal plexus (middle) and myenteric plexus (bottom). (f,g) Islet distribution within human pancreatic tissue. (f) A 2-mm-thick section of an adult human pancreas (top) was rendered transparent (bottom) with the PACT method. Briefly, a 2-mm-thick section was cut from a 4% PFA-fixed human pancreas, incubated in 0.5% PFA and 4% (wt/vol) acrylamide at 4 °C overnight and then polymerized in fresh A4P0 hydrogel monomer with 0.25% VA-044 thermal initiator for 2 h at 37 °C. The tissue was cleared with 4% SDS-PBS (pH 7.5) for 48 h, immunostained and mounted in sRIMS (~50% (wt/vol) sorbitol in 0.02 M PB, RI of 1.44). (g) The islet distribution was visualized by immunostaining for insulin (red), somatostatin (green) and DAPI (cyan) (see Table 4 for details on antibodies and nuclear stain); panels represent an imaging stack of 70 μm. Magnified regions are designated by yellow and blue boxes. Sparsely distributed islets are easily located with only 5× magnification (left). A group of islets were identified at 10× magnification (right, top), and a 3D image of a single islet was captured with a 25× magnification (right, bottom). All images were collected on a Zeiss LSM 780 confocal microscope with the Fluar 5× 0.25 NA M27 air objective (w.d. 12.5 mm), Plan-Apochromat 10× 0.45 NA M27 air objective (w.d. 2.0 mm) and the LD LCI Plan-Apochromat 25× 0.8 NA Imm Corr DIC M27 multi-immersion objective (w.d. 0.57 mm). Experiments on vertebrates conformed to all relevant governmental and institutional regulations, and they were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) and by the Office of Laboratory Animal Resources at the California Institute of Technology.